IL-2 receptor signaling is essential for the development of Klrg1+ terminally differentiated T regulatory cells
- PMID: 22786769
- PMCID: PMC3411868
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103768
IL-2 receptor signaling is essential for the development of Klrg1+ terminally differentiated T regulatory cells
Abstract
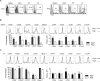
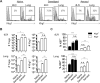
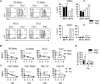
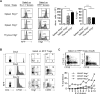
Thymic-derived natural T regulatory cells (Tregs) are characterized by functional and phenotypic heterogeneity. Recently, a small fraction of peripheral Tregs has been shown to express Klrg1, but it remains unclear as to what extent Klrg1 defines a unique Treg subset. In this study, we show that Klrg1(+) Tregs represent a terminally differentiated Treg subset derived from Klrg1(-) Tregs. This subset is a recent Ag-responsive and highly activated short-lived Treg population that expresses enhanced levels of Treg suppressive molecules and that preferentially resides within mucosal tissues. The development of Klrg1(+) Tregs also requires extensive IL-2R signaling. This activity represents a distinct function for IL-2, independent from its contribution to Treg homeostasis and competitive fitness. These and other properties are analogous to terminally differentiated short-lived CD8(+) T effector cells. Our findings suggest that an important pathway driving Ag-activated conventional T lymphocytes also operates for Tregs.
Figures

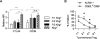
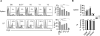



Similar articles
-
IL-2R signaling is essential for functional maturation of regulatory T cells during thymic development.J Immunol. 2013 Feb 15;190(4):1567-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201218. Epub 2013 Jan 11. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23315074 Free PMC article.
-
Murine autoimmune cholangitis requires two hits: cytotoxic KLRG1(+) CD8 effector cells and defective T regulatory cells.J Autoimmun. 2014 May;50:123-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2014.01.034. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Autoimmun. 2014. PMID: 24556277 Free PMC article.
-
KLRG1 impairs regulatory T-cell competitive fitness in the gut.Immunology. 2017 Sep;152(1):65-73. doi: 10.1111/imm.12749. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 28437578 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of regulatory T-cell heterogeneity in maintaining self-tolerance.Immunol Rev. 2014 May;259(1):103-14. doi: 10.1111/imr.12163. Immunol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24712462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T-cell tolerance and the multi-functional role of IL-2R signaling in T-regulatory cells.Immunol Rev. 2011 May;241(1):63-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01004.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21488890 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins Shape Treg Cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 28;13:865546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.865546. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35418975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recirculating Foxp3+ regulatory T cells are restimulated in the thymus under Aire control.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jun 9;79(7):355. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04328-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35678896 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine Signaling in the Development and Homeostasis of Regulatory T cells.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018 Mar 1;10(3):a028597. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028597. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018. PMID: 28620098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CD83 Molecule - An Important Immune Checkpoint.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 17;11:721. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00721. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32362900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual PD1/LAG3 immune checkpoint blockade limits tumor development in a murine model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Blood. 2018 Apr 5;131(14):1617-1621. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-06-792267. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29439955 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wing K, Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells exert checks and balances on self tolerance and autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2010;11:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Zhou L, Chong MM, Littman DR. Plasticity of CD4+ T cell lineage differentiation. Immunity. 2009;30:646–655. - PubMed
-
- Izcue A, Coombes JL, Powrie F. Regulatory lymphocytes and intestinal inflammation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009;27:313–338. - PubMed
-
- Itoh M, Takahashi T, Sakaguchi N, Kunioyasu Y, Shimizu J, Otsuka F, Sakaguchi S. Thymus and autoimmunity: Production of CD25+ CD4+ naturally anergic and suppressive T cells as a key function of the thymus in maintaining immunological self-tolerance. J. Immunol. 1999;162:5317–5326. - PubMed
-
- Thornton AM, Shevach EM. Suppressor effector function of CD4+ CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells is antigen nonspecific. J. Immunol. 2000;164:183–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

