Peptidomimetic Src/pretubulin inhibitor KX-01 alone and in combination with paclitaxel suppresses growth, metastasis in human ER/PR/HER2-negative tumor xenografts
- PMID: 22784709
- PMCID: PMC3462004
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0146
Peptidomimetic Src/pretubulin inhibitor KX-01 alone and in combination with paclitaxel suppresses growth, metastasis in human ER/PR/HER2-negative tumor xenografts
Abstract
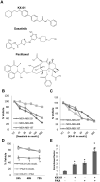
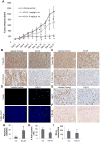
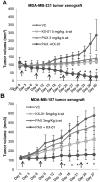
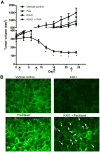
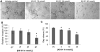
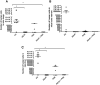
Src kinase is elevated in breast tumors that are ER/PR negative and do not overexpress HER2, but clinical trials with Src inhibitors have shown little activity. The present study evaluated preclinical efficacy of a novel peptidomimetic compound, KX-01 (KX2-391), that exhibits dual action as an Src and pretubulin inhibitor. KX-01 was evaluated as a single-agent and in combination with paclitaxel in MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-157, and MDA-MB-468 human ER/PR/HER2-negative breast cancer cells. Treatments were evaluated by growth/apoptosis, isobologram analysis, migration/invasion assays, tumor xenograft volume, metastasis, and measurement of Src, focal adhesion kinase (FAK), microtubules, Ki67, and microvessel density. KX-01 inhibited cell growth in vitro and in combination with paclitaxel resulted in synergistic growth inhibition. KX-01 resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-157 tumor xenografts (1 and 5 mg/kg, twice daily). KX-01 inhibited activity of Src and downstream mediator FAK in tumors that was coincident with reduced proliferation and angiogenesis and increased apoptosis. KX01 also resulted in microtubule disruption in tumors. Combination of KX-01 with paclitaxel resulted in significant regression of MDA-MB-231 tumors and reduced metastasis to mouse lung and liver. KX-01 is a potently active Src/pretubulin inhibitor that inhibits breast tumor growth and metastasis. As ER/PR/HER2-negative patients are candidates for paclitaxel therapy, combination with KX-01 may potentiate antitumor efficacy in management of this aggressive breast cancer subtype.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting SRC and tubulin in mucinous ovarian carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Dec 1;19(23):6532-43. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1305. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24100628 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Src Kinase/Pretubulin Inhibitor KX-01, Sensitizes ERα-negative Breast Cancers to Tamoxifen through ERα Reexpression.Mol Cancer Res. 2017 Nov;15(11):1491-1502. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0297-T. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Mol Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28751463 Free PMC article.
-
KX-01, a novel Src kinase inhibitor directed toward the peptide substrate site, synergizes with tamoxifen in estrogen receptor α positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Apr;132(2):391-409. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1513-3. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21509526
-
Inhibition of SRC family kinases and receptor tyrosine kinases by dasatinib: possible combinations in solid tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Sep 1;17(17):5546-52. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2616. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21670084 Review.
-
Dasatinib: a potent SRC inhibitor in clinical development for the treatment of solid tumors.Cancer Treat Rev. 2010 Oct;36(6):492-500. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.02.015. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Cancer Treat Rev. 2010. PMID: 20226597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting SRC and tubulin in mucinous ovarian carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Dec 1;19(23):6532-43. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1305. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24100628 Free PMC article.
-
Topical Tirbanibulin, a Dual Src Kinase and Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitor, for the Treatment of Plaque-Type Psoriasis: Phase I Results.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 11;14(10):2159. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102159. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297594 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidomimetics in cancer targeting.Mol Med. 2022 Dec 7;28(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00577-3. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36476230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Androgen receptor splice variants circumvent AR blockade by microtubule-targeting agents.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 15;6(27):23358-71. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4396. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26160840 Free PMC article.
-
Human adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells promote migration and early metastasis of triple negative breast cancer xenografts.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 28;9(2):e89595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089595. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L, Moore DT, Collichio F, et al. The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:2329–34. - PubMed
-
- Rodler E, Korde L, Gralow J. Current treatment options in triple negative breast cancer. Breast Dis. 2010;32:99–122. - PubMed
-
- Nabholtz JM, Gelmon K, Bontenbal M, Spielmann M, Catimel G, Conte P, et al. Multicenter, randomized comparative study of two doses of paclitaxel in patients with metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:1858–67. - PubMed
-
- Carey L, Winer E, Viale G, Cameron D, Gianni L. Triple-negative breast cancer: disease entity or title of convenience? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010;7:683–92. - PubMed
-
- Huang F, Reeves K, Han X, Fairchild C, Platero S, Wong TW, et al. Identification of candidate molecular markers predicting sensitivity in solid tumors to dasatinib: rationale for patient selection. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2226–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

