Regulation of hippocampus-dependent memory by the zinc finger protein Zbtb20 in mature CA1 neurons
- PMID: 22777671
- PMCID: PMC3487045
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.234187
Regulation of hippocampus-dependent memory by the zinc finger protein Zbtb20 in mature CA1 neurons
Abstract
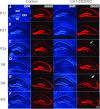
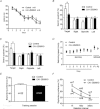
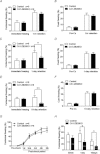
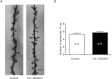
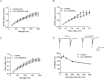
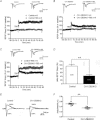
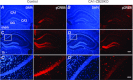
The mammalian hippocampus harbours neural circuitry that is crucial for associative learning and memory. The mechanisms that underlie the development and regulation of this complex circuitry are not fully understood. Our previous study established an essential role for the zinc finger protein Zbtb20 in the specification of CA1 field identity in the developing hippocampus. Here, we show that conditionally deleting Zbtb20 specifically in mature CA1 pyramidal neurons impaired hippocampus-dependent memory formation, without affecting hippocampal architecture or the survival, identity and basal excitatory synaptic activity of CA1 pyramidal neurons. We demonstrate that mature CA1-specific Zbtb20 knockout mice exhibited reductions in long-term potentiation (LTP) and NMDA receptor (NMDAR)-mediated excitatory post-synaptic currents. Furthermore, we show that activity-induced phosphorylation of ERK and CREB is impaired in the hippocampal CA1 of Zbtb20 mutant mice. Collectively, these results indicate that Zbtb20 in mature CA1 plays an important role in LTP and memory by regulating NMDAR activity, and activation of ERK and CREB.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deletion of LRRTM1 and LRRTM2 in adult mice impairs basal AMPA receptor transmission and LTP in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jun 5;115(23):E5382-E5389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803280115. Epub 2018 May 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29784826 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent activation of histamine H1 receptors in the hippocampal CA1 region enhances NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic excitation and long-term potentiation in astrocyte- and D-serine-dependent manner.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Jun;151:64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.03.036. Epub 2019 Mar 31. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30943384
-
Enhanced intrinsic excitability and EPSP-spike coupling accompany enriched environment-induced facilitation of LTP in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2012 Mar;107(5):1366-78. doi: 10.1152/jn.01009.2011. Epub 2011 Dec 7. J Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22157122
-
A Brief History of Long-Term Potentiation.Neuron. 2017 Jan 18;93(2):281-290. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.12.015. Neuron. 2017. PMID: 28103477 Review.
-
Hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and signal amplification of NMDA receptors.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):71-84. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.80. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725510 Review.
Cited by
-
Zbtb20 promotes astrocytogenesis during neocortical development.Nat Commun. 2016 Mar 22;7:11102. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11102. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27000654 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of Semaphorin 4C/Plexin-B2 signaling on fear memory via remodeling of neuronal and synaptic morphology.Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Apr;26(4):1376-1398. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0491-4. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 31444474 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analyses of adult mouse brain reveal enrichment of lncRNAs in specific brain regions and neuronal populations.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Mar 6;9:63. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00063. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25798087 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Transcriptome Landscape and Cell Fate Decoding in Human Brain Organoids after Transplantation.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jul;11(28):e2402287. doi: 10.1002/advs.202402287. Epub 2024 May 6. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38711218 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA-Associated Transcriptomic Changes in Resiliency or Susceptibility to Depression and Response to Antidepressant Treatment.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018 May 1;21(5):461-472. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyy010. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29390069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Benito E, Barco A. CREB's control of intrinsic and synaptic plasticity: implications for CREB-dependent memory models. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:230–240. - PubMed
-
- Brigman JL, Wright T, Talani G, Prasad-Mulcare S, Jinde S, Seabold GK, Mathur P, Davis MI, Bock R, Gustin RM, Colbran RJ, Alvarez VA, Nakazawa K, Delpire E, Lovinger DM, Holmes A. Loss of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors in CA1 hippocampus and cortex impairs long-term depression, reduces dendritic spine density, and disrupts learning. J Neurosci. 2010;30:4590–4600. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cull-Candy SG, Leszkiewicz DN. Role of distinct NMDA receptor subtypes at central synapses. Sci STKE. 2004;2004:re16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

