Cetuximab therapy in head and neck cancer: immune modulation with interleukin-12 and other natural killer cell-activating cytokines
- PMID: 22770960
- PMCID: PMC3432674
- DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2012.05.035
Cetuximab therapy in head and neck cancer: immune modulation with interleukin-12 and other natural killer cell-activating cytokines
Abstract
Background: Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN) is the sixth most common cancer worldwide. Greater than 90% of SCCHN of the oropharynx overexpress the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR or HER1). Cetuximab (Erbitux-TM) is a humanized anti-HER1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) that binds to HER1 overexpressing tumor cells. Cetuximab has a direct effect on HER1-positive cancer cells, but it also can activate immune cells that bear receptors for the Fc (constant portion) of IgG such as natural killer (NK) cells. NK cells have an activating Fc receptor for IgG (FcγRIIIa), which mediates Ab dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and enhances production of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in response to Ab-coated targets. Interleukin-12 (IL-12) is a cytokine produced by antigen-presenting cells that stimulates IFN-γ production from NK cells. We hypothesized that IL-12 would enhance the anti-tumor activity of cetuximab by activating the FcR effector mechanisms of NK cells.
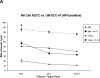
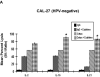
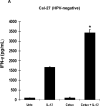
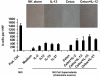
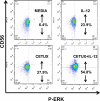
Methods: Expression of HER1 was measured on human papilloma virus (HPV)-positive (UD-SCC2, UM-SCC47) and HPV-negative (Cal27, UM-SCC74B) SCCHN cell lines by immunoblot analysis and flow cytometry. NK cells from normal donors were treated overnight with IL-2 (100 U), IL-12, IL-15, or IL-21 (all 10 ng/mL) and tested for ADCC versus cetuximab-coated cancer cells in a 4 hr (51)Cr assay. Release of cytokines by NK cells in response to cetuximab-coated cells was measured by ELISA. Phosphorylation of the ERK transcription factor in NK cells was measured by flow cytometry. The efficacy of combination therapy with cetuximab plus IL-12 was evaluated in a murine tumor model of head and neck cancer.
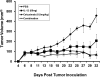
Results: All cell lines showed >99% expression of HER1 by flow cytometry and immunoblot analysis except UM-SCC74B (73%). Normal NK cells mediated 49.4% lysis of cetuximab-coated SCCHN cell lines as compared to 7.6% lysis of cells treated with control IgG (P = .0002). NK cell lysis of cetuximab-coated SCCHN cells was markedly enhanced by 12 hr pre-treatment of NK cells with IL-12 (71.6% lysis, P = .005 vs cetuximab alone). As a control, IL-12-activated NK cells were tested against IgG-treated cells. ADCC under these conditions was just 21.7%. Similar levels of lysis were noted for both HPV-positive and HPV-negative and cell lines. Other NK cell activating factors such as IL-2, IL-15, and IL-21 were also able to enhance NK cell ADCC. The stimulus of IL-12 and cetuximab-coated tumor cells induced the synergistic production of nanogram levels of IFN-γ (>6-fold increase over controls) (P < .001). A similar effect was seen for NK cell production of the chemokines RANTES, MIP-1α, and IL-8. Phosphorylation of ERK (which is critical for FcR-mediated ADCC and cytokine production) was enhanced in NK cells exposed to IL-12 and IgG as compared to control conditions. The combination of cetuximab plus IL-12 resulted in a reduction in tumor burden when compared to either agent alone in a murine xenograft model of SCCHN.
Conclusion: Cytokine stimulation of NK cells in the presence of cetuximab-coated head and neck cancer cells leads to enhanced NK cell mediated ADCC and cytokine secretion independent of tumor cell HPV-status. Cytokine administration could be a useful adjuvant in the cetuximab treatment of HER1-positive head and neck cancer.
Copyright © 2012 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures








Similar articles
-
An IL-15-based superagonist ALT-803 enhances the NK cell response to cetuximab-treated squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019 Aug;68(8):1379-1389. doi: 10.1007/s00262-019-02372-2. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019. PMID: 31338557 Free PMC article.
-
The activation of natural killer cell effector functions by cetuximab-coated, epidermal growth factor receptor positive tumor cells is enhanced by cytokines.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Nov 1;13(21):6419-28. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0865. Epub 2007 Oct 25. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17962339
-
Role of polymorphic Fc gamma receptor IIIa and EGFR expression level in cetuximab mediated, NK cell dependent in vitro cytotoxicity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009 Nov;58(11):1853-64. doi: 10.1007/s00262-009-0697-4. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009. PMID: 19319529 Free PMC article.
-
The Right Partner in Crime: Unlocking the Potential of the Anti-EGFR Antibody Cetuximab via Combination With Natural Killer Cell Chartering Immunotherapeutic Strategies.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 7;12:737311. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.737311. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34557197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor microenvironmental modification by the current target therapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 May 5;42(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02691-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37143088 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A view on EGFR-targeted therapies from the oncogene-addiction perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2013 Apr 26;4:53. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00053. eCollection 2013. Front Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23637683 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-12 in multimodal tumor therapies for induction of anti-tumor immunity.Discov Oncol. 2024 May 16;15(1):170. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01011-2. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38753073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Memory-like Differentiation, Tumor-Targeting mAbs, and Chimeric Antigen Receptors Enhance Natural Killer Cell Responses to Head and Neck Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Oct 13;29(20):4196-4208. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-0156. Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37556118 Free PMC article.
-
The EGFR-P38 MAPK axis up-regulates PD-L1 through miR-675-5p and down-regulates HLA-ABC via hexokinase-2 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021 Jan;41(1):62-78. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12117. Epub 2021 Jan 1. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34236149 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Magnetic Nanoparticles for Mechanical Lysis of Tumor Cells by Low-Amplitude Alternating Magnetic Field.Materials (Basel). 2016 Nov 22;9(11):943. doi: 10.3390/ma9110943. Materials (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28774062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haddad RI, Shin DM. Recent advances in head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008;359:1143–54. - PubMed
-
- Colevas AD. Chemotherapy options for patients with metastatic or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:2644–52. - PubMed
-
- Vermorken JB, Specenier P. Optimal treatment for recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancer. Ann Oncol. 2010;(Suppl 7):vii252–vii261. - PubMed
-
- Dassonville O, Formento JL, Francoual M, Ramaioli A, Santini J, Schneider M, Demard F, Milano G. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and survival in upper aerodigestive tract cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1993;11:1873–78. - PubMed
-
- Vermorken JB, Trigo J, Hitt R, Koralewski P, Diaz-Rubio E, Rolland F, Knecht R, Amellal N, Schueler A, Baselga J. Open-label, uncontrolled, multicenter phase II study to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of cetuximab as a single agent in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck who failed to respond to platinum-based therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007;25:2171–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

