Leukocyte rolling on P-selectin: a three-dimensional numerical study of the effect of cytoplasmic viscosity
- PMID: 22768931
- PMCID: PMC3328691
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.03.018
Leukocyte rolling on P-selectin: a three-dimensional numerical study of the effect of cytoplasmic viscosity
Abstract
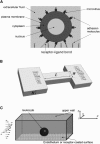
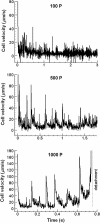
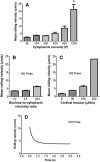
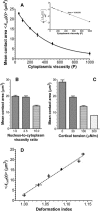
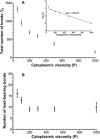
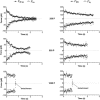
Rolling leukocytes deform and show a large area of contact with endothelium under physiological flow conditions. We studied the effect of cytoplasmic viscosity on leukocyte rolling using our three-dimensional numerical algorithm that treats leukocyte as a compound droplet in which the core phase (nucleus) and the shell phase (cytoplasm) are viscoelastic fluids. The algorithm includes the mechanical properties of the cell cortex by cortical tension and considers leukocyte microvilli that deform viscoelastically and form viscous tethers at supercritical force. Stochastic binding kinetics describes binding of adhesion molecules. The leukocyte cytoplasmic viscosity plays a critical role in leukocyte rolling on an adhesive substrate. High-viscosity cells are characterized by high mean rolling velocities, increased temporal fluctuations in the instantaneous velocity, and a high probability for detachment from the substrate. A decrease in the rolling velocity, drag, and torque with the formation of a large, flat contact area in low-viscosity cells leads to a dramatic decrease in the bond force and stable rolling. Using values of viscosity consistent with step aspiration studies of human neutrophils (5-30 Pa·s), our computational model predicts the velocities and shape changes of rolling leukocytes as observed in vitro and in vivo.
Copyright © 2012 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of cell deformation on leukocyte rolling adhesion in shear flow.J Biomech Eng. 1999 Dec;121(6):636-43. doi: 10.1115/1.2800866. J Biomech Eng. 1999. PMID: 10633265
-
Roles of cell and microvillus deformation and receptor-ligand binding kinetics in cell rolling.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Oct;295(4):H1439-50. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.91536.2007. Epub 2008 Jul 25. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18660437 Free PMC article.
-
A 3-D computational model predicts that cell deformation affects selectin-mediated leukocyte rolling.Biophys J. 2005 Jan;88(1):96-104. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.051029. Epub 2004 Oct 15. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15489302 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil rolling at high shear: flattening, catch bond behavior, tethers and slings.Mol Immunol. 2013 Aug;55(1):59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.10.025. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23141302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomechanics of leukocyte rolling.Biorheology. 2011;48(1):1-35. doi: 10.3233/BIR-2011-0579. Biorheology. 2011. PMID: 21515934 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Localization of Rolling and Firm-Adhesive Interactions Between Circulating Tumor Cells and the Microvasculature Wall.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2020 Jan 24;13(2):141-154. doi: 10.1007/s12195-020-00610-7. eCollection 2020 Apr. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2020. PMID: 32175027 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of computational models to better understand microvascular remodelling: a focus on biomechanical integration across scales.Interface Focus. 2015 Apr 6;5(2):20140077. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2014.0077. Interface Focus. 2015. PMID: 25844149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping cell surface adhesion by rotation tracking and adhesion footprinting.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 14;7:44502. doi: 10.1038/srep44502. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28290531 Free PMC article.
-
Elongation Index as a Sensitive Measure of Cell Deformation in High-Throughput Microfluidic Systems.Biophys J. 2020 Aug 4;119(3):493-501. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.06.027. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 32697978 Free PMC article.
-
Deformable cell-cell and cell-substrate interactions in semi-infinite domain.J Biomech. 2013 Apr 5;46(6):1067-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2013.01.027. Epub 2013 Mar 5. J Biomech. 2013. PMID: 23481422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim M.B., Sarelius I.H. Role of shear forces and adhesion molecule distribution on P-selectin-mediated leukocyte rolling in postcapillary venules. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004;287:H2705–H2711. - PubMed
-
- Norman K.E., Moore K.L., Ley K. Leukocyte rolling in vivo is mediated by P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1. Blood. 1995;86:4417–4421. - PubMed
-
- Norman K.E., Katopodis A.G., Hellewell P.G. P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 supports rolling on E- and P-selectin in vivo. Blood. 2000;96:3585–3591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

