Serotonin transporter inhibition attenuates l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia without compromising l-DOPA efficacy in hemi-parkinsonian rats
- PMID: 22762478
- PMCID: PMC3445783
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08202.x
Serotonin transporter inhibition attenuates l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia without compromising l-DOPA efficacy in hemi-parkinsonian rats
Abstract
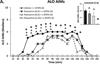
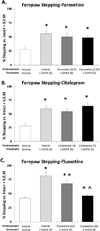
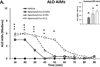
Long-term dopamine replacement therapy with l-DOPA in Parkinson's disease often leads to the development of abnormal involuntary movements known as l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Growing evidence suggests that, following dopamine cell loss, serotonin neurons acting as surrogates for dopaminergic processes take up l-DOPA, convert it to dopamine and release it in an unregulated fashion that precipitates dyskinesia. Although most studies have focused on serotonin 5-HT(1) receptor stimulation as an antidyskinetic strategy, targeting the serotonin transporter modulation of dopamine activity has been overlooked. Therefore, in the current study, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors were tested for their ability to reduce l-DOPA- and apomorphine-induced dyskinesia. In Experiments 1 and 2, hemi-parkinsonian rats were primed with l-DOPA until stable dyskinesia developed. Rats in Experiment 1 were administered the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors paroxetine, citalopram or fluoxetine, followed by l-DOPA. Abnormal involuntary movements and forepaw adjusting steps were recorded to determine the effects of these compounds on dyskinesia and motor performance, respectively. Brains were collected on the final test day, after which striatal and raphe monoamines were examined via high-performance liquid chromatography. In Experiment 2, dyskinesias were measured after selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and apomorphine. Serotonin reuptake inhibitors dose-dependently attenuated l-DOPA- but not apomorphine-induced dyskinesia, and preserved l-DOPA efficacy. Neurochemically, serotonin transporter inhibition enhanced striatal and raphe serotonin levels and reduced its turnover, indicating a potential mechanism of action. The present results support targeting serotonin transporters to improve Parkinson's disease treatment and provide further evidence for the role of the serotonin system in l-DOPA's effects.
© 2012 The Authors. European Journal of Neuroscience © 2012 Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Effects of prolonged selective serotonin reuptake inhibition on the development and expression of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in hemi-parkinsonian rats.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Feb;77:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.09.017. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24067924 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse serotonin actions of vilazodone reduce l-3,4-dihidroxyphenylalanine-induced dyskinesia in hemi-parkinsonian rats.Mov Disord. 2018 Nov;33(11):1740-1749. doi: 10.1002/mds.100. Mov Disord. 2018. PMID: 30485908
-
Effect of tricyclic antidepressants on L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia and motor improvement in hemi-parkinsonian rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2016 Mar;142:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2016.01.004. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2016. PMID: 26791104
-
Serotonin/dopamine interaction in the induction and maintenance of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia: An update.Prog Brain Res. 2021;261:287-302. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2021.01.032. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Prog Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33785132 Review.
-
Adjuncts to dopamine replacement: a pragmatic approach to reducing the problem of dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease.Mov Disord. 1998 Nov;13(6):871-6. doi: 10.1002/mds.870130603. Mov Disord. 1998. PMID: 9827609 Review.
Cited by
-
Serotonergic system modulation holds promise for L-DOPA-induced dyskinesias in hemiparkinsonian rats: A systematic review.EXCLI J. 2020 Mar 2;19:268-295. doi: 10.17179/excli2020-1024. eCollection 2020. EXCLI J. 2020. PMID: 32327954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin System Implication in l-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia: From Animal Models to Clinical Investigations.Front Neurol. 2014 May 20;5:78. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2014.00078. eCollection 2014. Front Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24904522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in Parkinson's Disease: An Overview on Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, Therapy Management Strategies and Future Directions.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 30;12(13):4427. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134427. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The acute and long-term L-DOPA effects are independent from changes in the activity of dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons in 6-OHDA lesioned rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Jul;173(13):2135-46. doi: 10.1111/bph.13447. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26805402 Free PMC article.
-
Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson's Disease: Pathogenesis and Emerging Treatment Strategies.Cells. 2022 Nov 23;11(23):3736. doi: 10.3390/cells11233736. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36496996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahlskog JE, Muenter MD. Frequency of levodopa-related dyskinesias and motor fluctuations as estimated from the cumulative literature. Mov Disord. 2001;16(3):448–458. - PubMed
-
- Arai R, Karasawa N, Geffard M, Nagatsu I. L-DOPA is converted to dopamine in serotonergic fibers of the striatum of the rat: a double-labeling immunofluorescence study. Neurosci Lett. 1995;195(3):195–198. - PubMed
-
- Bara-Jimenez W, Bibbiani F, Morris MJ, Dimitrova T, Sherzai A, Mouradian MM, Chase TN. Effects of serotonin 5-HT1A agonist in advanced Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2005;20(8):932–936. - PubMed
-
- Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O. The L-3,4-dioxyphenylalanine (DOPA)-effect in Parkinson-akinesia. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1961;73:787–788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

