FoxQ1 overexpression influences poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer, associates with the phenomenon of EMT
- PMID: 22761930
- PMCID: PMC3386178
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039937
FoxQ1 overexpression influences poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer, associates with the phenomenon of EMT
Abstract
Background: We determined the expression of forkhead box Q1 (FoxQ1), E-cadherin (E-cad), Mucin 1 (MUC1), vimentin (VIM) and S100 calcium binding protein A4 (S100A4), all epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) indicator proteins in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissue samples. We also investigated the relationship between these five proteins expression and other clinicopathologic factors in NSCLC. Finally, we assessed the potential value of these markers as prognostic indicators of survival in NSCLC's patients.
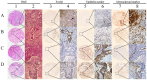
Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry were used to characterize the expression of the FoxQ1 mRNA and protein in NSCLC. Expression of transcripts and translated products for the other four EMT indicator proteins was assessed by immunohistochemistry in the same clinical NSCLC samples.
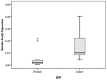
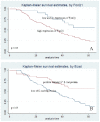
Results: FoxQ1 mRNA and protein were up-regulated in NSCLC compared with normal tissues (P = 0.015 and P<0.001, respectively). Expression of FoxQ1 in adenocarcinoma was higher than in squamous cell carcinoma (P = 0.005), and high expression of FoxQ1 correlated with loss of E-cad expression (P = 0.012), and anomalous positivity of VIM (P = 0.024) and S100A4 (P = 0.004). Additional survival analysis showed that high expression of FoxQ1 (P = 0.047) and E-cad (P = 0.021) were independent prognostic factors.
Conclusion: FoxQ1 maybe plays a specific role in the EMT of NSCLC, and could be used as a prognostic factor for NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potentiality of forkhead box Q1 as a biomarker for monitoring tumor features and predicting prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jan;34(1):e23031. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23031. Epub 2019 Nov 12. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 31713908 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of FoxQ1 in NSCLC through regulating EMT and increasing chemosensitivity.Oncotarget. 2014 Oct 30;5(20):9689-702. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2103. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25356753 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal expression of EMT-related proteins, S100A4, vimentin and E-cadherin, is correlated with clinicopathological features and prognosis in HCC.Med Oncol. 2014 Jun;31(6):970. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0970-z. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24781336
-
Epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a mutual association with airway disease.Med Oncol. 2017 Mar;34(3):45. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-0900-y. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Med Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28197929
-
Short hairpin RNA targeting FOXQ1 inhibits invasion and metastasis via the reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer.Int J Oncol. 2013 Apr;42(4):1271-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1807. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23403865
Cited by
-
The hepatic FOXQ1 transcription factor regulates glucose metabolism in mice.Diabetologia. 2016 Oct;59(10):2229-39. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-4043-z. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 27421728
-
The microRNA expression signature of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by RNA sequencing: anti-tumour functions of the microRNA-216 cluster.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 26;8(41):70097-70115. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19591. eCollection 2017 Sep 19. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29050264 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value and clinicopathological significance of epithelial cadherin expression in non-small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2015 Sep;6(5):589-96. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12227. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Thorac Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26445607 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated expression of SHIP2 correlates with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013 Sep 15;6(10):2185-91. eCollection 2013. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 24133597 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MALAT1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis by targeting miR-124/foxq1 in bladder transitional cell carcinoma (BTCC).Am J Cancer Res. 2018 Apr 1;8(4):748-760. eCollection 2018. Am J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29736319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cagle PT, Allen TC, Dacic S, Beasley MB, Borczuk AC, et al. Revolution in lung cancer: new challenges for the surgical pathologist. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:110–116. - PubMed
-
- Wen C, Dehnel T. China wrestles with lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:15. - PubMed
-
- Gao W, Liu L, Lu X, Shu Y. Circulating microRNAs: possible prediction biomarkers for personalized therapy of non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Clin Lung Cancer. 2011;12:14–17. - PubMed
-
- Smith CB, Kelley AS, Meier DE. Evidence for new standard of care in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;22:193–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

