HEMD: an integrated tool of human epigenetic enzymes and chemical modulators for therapeutics
- PMID: 22761927
- PMCID: PMC3382562
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039917
HEMD: an integrated tool of human epigenetic enzymes and chemical modulators for therapeutics
Abstract
Background: Epigenetic mechanisms mainly include DNA methylation, post-translational modifications of histones, chromatin remodeling and non-coding RNAs. All of these processes are mediated and controlled by enzymes. Abnormalities of the enzymes are involved in a variety of complex human diseases. Recently, potent natural or synthetic chemicals are utilized to establish the quantitative contributions of epigenetic regulation through the enzymes and provide novel insight for developing new therapeutics. However, the development of more specific and effective epigenetic therapeutics requires a more complete understanding of the chemical epigenomic landscape.
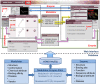
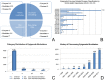
Description: Here, we present a human epigenetic enzyme and modulator database (HEMD), the database which provides a central resource for the display, search, and analysis of the structure, function, and related annotation for human epigenetic enzymes and chemical modulators focused on epigenetic therapeutics. Currently, HEMD contains 269 epigenetic enzymes and 4377 modulators in three categories (activators, inhibitors, and regulators). Enzymes are annotated with detailed description of epigenetic mechanisms, catalytic processes, and related diseases, and chemical modulators with binding sites, pharmacological effect, and therapeutic uses. Integrating the information of epigenetic enzymes in HEMD should allow for the prediction of conserved features for proteins and could potentially classify them as ideal targets for experimental validation. In addition, modulators curated in HEMD can be used to investigate potent epigenetic targets for the query compound and also help chemists to implement structural modifications for the design of novel epigenetic drugs.
Conclusions: HEMD could be a platform and a starting point for biologists and medicinal chemists for furthering research on epigenetic therapeutics. HEMD is freely available at http://mdl.shsmu.edu.cn/HEMD/.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
ASD: a comprehensive database of allosteric proteins and modulators.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D663-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1022. Epub 2010 Nov 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21051350 Free PMC article.
-
HEDD: the human epigenetic drug database.Database (Oxford). 2016 Dec 26;2016:baw159. doi: 10.1093/database/baw159. Print 2016. Database (Oxford). 2016. PMID: 28025347 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical regulation of epigenetic modifications: opportunities for new cancer therapy.Med Res Rev. 2008 Sep;28(5):645-87. doi: 10.1002/med.20120. Med Res Rev. 2008. PMID: 18271058 Review.
-
MetaImprint: an information repository of mammalian imprinted genes.Development. 2014 Jun;141(12):2516-23. doi: 10.1242/dev.105320. Epub 2014 May 21. Development. 2014. PMID: 24850854
-
Peptides as epigenetic modulators: therapeutic implications.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 Jul 12;11(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0700-7. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31300053 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Computational Approach for the Discovery of Novel DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitors.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 16;46(4):3394-3407. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040213. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666943 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme Databases in the Era of Omics and Artificial Intelligence.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 29;24(23):16918. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316918. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Usefulness of Melatonin and Other Compounds as Antioxidants and Epidrugs in the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Dec 24;11(1):35. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010035. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EpiDBase: a manually curated database for small molecule modulators of epigenetic landscape.Database (Oxford). 2015 Mar 16;2015:bav013. doi: 10.1093/database/bav013. Print 2015. Database (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 25776023 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Modulators as Potential Multi-targeted Drugs Against Hedgehog Pathway for Treatment of Cancer.Protein J. 2019 Oct;38(5):537-550. doi: 10.1007/s10930-019-09832-9. Protein J. 2019. PMID: 30993446
References
-
- Bird A. Perceptions of epigenetics. Nature. 2007;447:396–398. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg AD, Allis CD, Bernstein E. Epigenetics: a landscape takes shape. Cell. 2007;128:635–638. - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Zhou H, Hu H, Lai M. Non-coding RNAs and their epigenetic regulatory mechanisms. Biol Cell. 2010;102:645–655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

