Structural diversity and African origin of the 17q21.31 inversion polymorphism
- PMID: 22751100
- PMCID: PMC3408829
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2335
Structural diversity and African origin of the 17q21.31 inversion polymorphism
Abstract
The 17q21.31 inversion polymorphism exists either as direct (H1) or inverted (H2) haplotypes with differential predispositions to disease and selection. We investigated its genetic diversity in 2,700 individuals, with an emphasis on African populations. We characterize eight structural haplotypes due to complex rearrangements that vary in size from 1.08-1.49 Mb and provide evidence for a 30-kb H1-H2 double recombination event. We show that recurrent partial duplications of the KANSL1 gene have occurred on both the H1 and H2 haplotypes and have risen to high frequency in European populations. We identify a likely ancestral H2 haplotype (H2') lacking these duplications that is enriched among African hunter-gatherer groups yet essentially absent from West African populations. Whereas H1 and H2 segmental duplications arose independently and before human migration out of Africa, they have reached high frequencies recently among Europeans, either because of extraordinary genetic drift or selective sweeps.
Figures
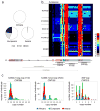
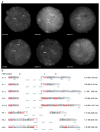

Similar articles
-
Structural haplotypes and recent evolution of the human 17q21.31 region.Nat Genet. 2012 Jul 1;44(8):881-5. doi: 10.1038/ng.2334. Nat Genet. 2012. PMID: 22751096 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent inversion events at 17q21.31 microdeletion locus are linked to the MAPT H2 haplotype.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2010;129(4):275-9. doi: 10.1159/000315901. Epub 2010 Jul 6. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2010. PMID: 20606400 Free PMC article.
-
Reassessing the Evolutionary History of the 17q21 Inversion Polymorphism.Genome Biol Evol. 2015 Nov 11;7(12):3239-48. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv214. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 26560338 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the complex role of MAPT-containing H1 and H2 haplotypes in neurodegenerative diseases.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 May 29;19(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00731-x. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 38812061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence suggesting that Homo neanderthalensis contributed the H2 MAPT haplotype to Homo sapiens.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Aug;33(Pt 4):582-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0330582. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16042549 Review.
Cited by
-
Neolithic expansion and the 17q21.31 inversion in Iberia: an evolutionary approach to H2 haplotype distribution in the Near East and Europe.Mol Genet Genomics. 2023 Jan;298(1):153-160. doi: 10.1007/s00438-022-01969-0. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Mol Genet Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36355195 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression, methylation and neuropathology correlations at progressive supranuclear palsy risk loci.Acta Neuropathol. 2016 Aug;132(2):197-211. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1576-7. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Acta Neuropathol. 2016. PMID: 27115769 Free PMC article.
-
17q21.31 sub-haplotypes underlying H1-associated risk for Parkinson's disease are associated with LRRC37A/2 expression in astrocytes.Mol Neurodegener. 2022 Jul 15;17(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00551-x. Mol Neurodegener. 2022. PMID: 35841044 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome sequencing of Turkish genomes reveals functional private alleles and impact of genetic interactions with Europe, Asia and Africa.BMC Genomics. 2014 Nov 7;15(1):963. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-963. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25376095 Free PMC article.
-
Tau haplotypes support the Asian ancestry of the Roma population settled in the Basque Country.Heredity (Edinb). 2018 Jan;120(2):91-99. doi: 10.1038/s41437-017-0001-x. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Heredity (Edinb). 2018. PMID: 29225349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tuzun E, et al. Fine-scale structural variation of the human genome. Nat Genet. 2005;37:727–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- F32HG006070/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HG00035/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HG000044/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM097807/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000035/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG002385/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG004120/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000044/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HG006070/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002385/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HG004120/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 ES022577/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- F32GM097807/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI_/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States

