Oct-1 acts as a transcriptional repressor on the C-reactive protein promoter
- PMID: 22750226
- PMCID: PMC3401324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.06.005
Oct-1 acts as a transcriptional repressor on the C-reactive protein promoter
Abstract
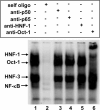
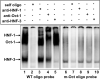
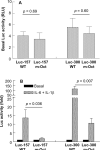
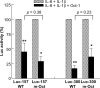
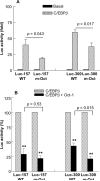
C-reactive protein (CRP), a plasma protein of the innate immune system, is produced by hepatocytes. A critical regulatory region (-42 to -57) on the CRP promoter contains binding site for the IL-6-activated transcription factor C/EBPβ. The IL-1β-activated transcription factor NF-κB binds to a κB site located nearby (-63 to -74). The κB site overlaps an octamer motif (-59 to -66) which is the binding site for the constitutively active transcription factor Oct-1. Oct-1 is known to function both as a transcriptional repressor and as an activator depending upon the promoter context. Also, Oct-1 can regulate gene expression either by binding directly to the promoter or by interacting with other transcription factors bound to the promoter. The aim of this study was to investigate the functions of Oct-1 in regulating CRP expression. In luciferase transactivation assays, overexpressed Oct-1 inhibited (IL-6+IL-1β)-induced CRP expression in Hep3B cells. Deletion of the Oct-1 site from the promoter drastically reduced the cytokine response because the κB site was altered as a consequence of deleting the Oct-1 site. Surprisingly, overexpressed Oct-1 inhibited the residual (IL-6+IL-1β)-induced CRP expression through the promoter lacking the Oct-1 site. Similarly, deletion of the Oct-1 site reduced the induction of CRP expression in response to overexpressed C/EBPβ, and overexpressed Oct-1 inhibited C/EBPβ-induced CRP expression through the promoter lacking the Oct-1 site. We conclude that Oct-1 acts as a transcriptional repressor of CRP expression and it does so by occupying its cognate site on the promoter and also via other transcription factors by an as yet undefined mechanism.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

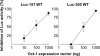
Similar articles
-
A novel RBP-J kappa-dependent switch from C/EBP beta to C/EBP zeta at the C/EBP binding site on the C-reactive protein promoter.J Immunol. 2007 Jun 1;178(11):7302-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.11.7302. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17513780 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of basal and induced expression of C-reactive protein through an overlapping element for OCT-1 and NF-kappaB on the proximal promoter.J Immunol. 2005 Sep 1;175(5):3386-90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.5.3386. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16116232 Free PMC article.
-
Transactivation of C-reactive protein by IL-6 requires synergistic interaction of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta (C/EBP beta) and Rel p50.J Immunol. 2001 Feb 15;166(4):2378-84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.4.2378. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11160296
-
Overexpressed nuclear factor-kappaB can participate in endogenous C-reactive protein induction, and enhances the effects of C/EBPbeta and signal transducer and activator of transcription-3.Immunology. 2003 Apr;108(4):539-47. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01608.x. Immunology. 2003. PMID: 12667216 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1beta stimulates acute phase response and C-reactive protein synthesis by inducing an NFkappaB- and C/EBPbeta-dependent autocrine interleukin-6 loop.Mol Immunol. 2008 May;45(9):2678-89. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.12.017. Epub 2008 Feb 8. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18262272
Cited by
-
Mutations on a conserved distal enhancer in the porcine C-reactive protein gene impair its expression in liver.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 14;14:1250942. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1250942. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37781386 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional cross talk between orphan nuclear receptor ERRγ and transmembrane transcription factor ATF6α coordinates endoplasmic reticulum stress response.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Aug;41(14):6960-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt429. Epub 2013 May 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23716639 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the phosphocholine-binding site of human C-reactive protein by site-directed mutagenesis.J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25353-8. J Biol Chem. 1992. PMID: 1460031 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory markers in ulcerative colitis: Current insights and future advances.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015 Feb 15;6(1):13-22. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i1.13. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25685607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic association and functional implications of TLR4 rs1927914 polymorphism on colon cancer risk.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jul 18;24(1):858. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12604-z. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39026223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal A, Cha-Molstad H, Samols D, Kushner I. Transactivation of C-reactive protein by IL-6 requires synergistic interaction of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β (C/EBPβ) and Rel p50. J. Immunol. 2001;166:2378–2384. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal A, Samols D, Kushner I. Transcription factor c-Rel enhances C-reactive protein expression by facilitating the binding of C/EBPβ to the promoter. Mol. Immunol. 2003b;40:373–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

