PcrA-mediated disruption of RecA nucleoprotein filaments--essential role of the ATPase activity of RecA
- PMID: 22743269
- PMCID: PMC3458574
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks641
PcrA-mediated disruption of RecA nucleoprotein filaments--essential role of the ATPase activity of RecA
Abstract
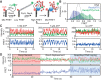
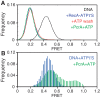
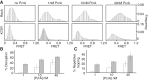
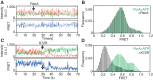
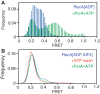
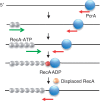
The essential DNA helicase, PcrA, regulates recombination by displacing the recombinase RecA from the DNA. The nucleotide-bound state of RecA determines the stability of its nucleoprotein filaments. Using single-molecule fluorescence approaches, we demonstrate that RecA displacement by a translocating PcrA requires the ATPase activity of the recombinase. We also show that in a 'head-on collision' between a polymerizing RecA filament and a translocating PcrA, the RecA K72R ATPase mutant, but not wild-type RecA, arrests helicase translocation. Our findings demonstrate that translocation of PcrA is not sufficient to displace RecA from the DNA and assigns an essential role for the ATPase activity of RecA in helicase-mediated disruption of its filaments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Active displacement of RecA filaments by UvrD translocase activity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Apr 30;43(8):4133-49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv186. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25824953 Free PMC article.
-
PcrA helicase dismantles RecA filaments by reeling in DNA in uniform steps.Cell. 2010 Aug 20;142(4):544-55. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.016. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20723756 Free PMC article.
-
DNA helicase activity of PcrA is not required for the displacement of RecA protein from DNA or inhibition of RecA-mediated strand exchange.J Bacteriol. 2007 Jun;189(12):4502-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00376-07. Epub 2007 Apr 20. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17449621 Free PMC article.
-
Expedient placement of two fluorescent dyes for investigating dynamic DNA protein interactions in real time.Chromosome Res. 2008;16(3):451-67. doi: 10.1007/s10577-008-1235-5. Chromosome Res. 2008. PMID: 18461484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of bacterial RecA protein function.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Jan-Feb;42(1):41-63. doi: 10.1080/10409230701260258. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17364684 Review.
Cited by
-
The B. subtilis Accessory Helicase PcrA Facilitates DNA Replication through Transcription Units.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jun 12;11(6):e1005289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005289. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26070154 Free PMC article.
-
Active displacement of RecA filaments by UvrD translocase activity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Apr 30;43(8):4133-49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv186. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25824953 Free PMC article.
-
Translocation-coupled DNA cleavage by the Type ISP restriction-modification enzymes.Nat Chem Biol. 2015 Nov;11(11):870-7. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1926. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Nat Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 26389736 Free PMC article.
-
Cas3 Protein-A Review of a Multi-Tasking Machine.Genes (Basel). 2020 Feb 18;11(2):208. doi: 10.3390/genes11020208. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32085454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacillus subtilis PcrA Couples DNA Replication, Transcription, Recombination and Segregation.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Jul 21;7:140. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00140. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32793628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lohman T, Tomko E, Wu C. Non-hexameric DNA helicases and translocases: mechanisms and regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008;9:391–401. - PubMed
-
- Singleton MR, Dillingham MS, Wigley DB. Structure and mechanism of helicases and nucleic acid translocases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007;76:23–50. - PubMed
-
- Benkovic S, Valentine A, Salinas F. Replisome-mediated DNA replication. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001;70:181–208. - PubMed
-
- Bidnenko V, Lestini R, Michel B. The Escherichia coli UvrD helicase is essential for Tus removal during recombination-dependent replication restart from Ter sites. Mol. Microbiol. 2006;62:382–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

