Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in pathogenesis of vascular complications of diabetes
- PMID: 22737658
- PMCID: PMC3380122
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2012.36.3.190
Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in pathogenesis of vascular complications of diabetes
Abstract
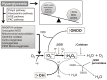
Macrovascular and microvascular diseases are currently the principal causes of morbidity and mortality in subjects with diabetes. Disorders of the physiological signaling functions of reactive oxygen species (superoxide and hydrogen peroxide) and reactive nitrogen species (nitric oxide and peroxynitrite) are important features of diabetes. In the absence of an appropriate compensation by the endogenous antioxidant defense network, increased oxidative stress leads to the activation of stress-sensitive intracellular signaling pathways and the formation of gene products that cause cellular damage and contribute to the vascular complications of diabetes. It has recently been suggested that diabetic subjects with vascular complications may have a defective cellular antioxidant response against the oxidative stress generated by hyperglycemia. This raises the concept that antioxidant therapy may be of great benefit to these subjects. Although our understanding of how hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress ultimately leads to tissue damage has advanced considerably in recent years, effective therapeutic strategies to prevent or delay the development of this damage remain limited. Thus, further investigation of therapeutic interventions to prevent or delay the progression of diabetic vascular complications is needed.
Keywords: Diabetic vascular complications; Reactive nitrogen species; Reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of vascular reactive oxygen species in development of vascular abnormalities in diabetes.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007 Sep;77 Suppl 1:S65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2007.01.036. Epub 2007 Apr 27. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007. PMID: 17467110 Review.
-
Hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and its role in diabetes mellitus related cardiovascular diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(32):5695-703. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319320005. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23448484 Review.
-
Dysregulation of nitric oxide synthases during early and late pathophysiological conditions of diabetes mellitus leads to amassing of microvascular impedement.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021 Apr 21;20(1):989-1002. doi: 10.1007/s40200-021-00799-y. eCollection 2021 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 34178871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress and diabetic vascular complications.Diabetes Care. 1996 Mar;19(3):257-67. doi: 10.2337/diacare.19.3.257. Diabetes Care. 1996. PMID: 8742574 Review.
-
The Role of Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Neuropathy: Generation of Free Radical Species in the Glycation Reaction and Gene Polymorphisms Encoding Antioxidant Enzymes to Genetic Susceptibility to Diabetic Neuropathy in Population of Type I Diabetic Patients.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015 Apr;71(3):1425-43. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0365-y. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25427889
Cited by
-
The novel mitochondria-targeted hydrogen sulfide (H2S) donors AP123 and AP39 protect against hyperglycemic injury in microvascular endothelial cells in vitro.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Nov;113(Pt A):186-198. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.08.019. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27565382 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb repressive complex 2 regulates MiR-200b in retinal endothelial cells: potential relevance in diabetic retinopathy.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 17;10(4):e0123987. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123987. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25884496 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiabetic activity of 3-hydroxyflavone analogues in high fructose fed insulin resistant rats.EXCLI J. 2014 Sep 9;13:1055-74. eCollection 2014. EXCLI J. 2014. PMID: 26417321 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk Between Oxidative Stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress in Endothelial Dysfunction and Aberrant Angiogenesis Associated With Diabetes: A Focus on the Protective Roles of Heme Oxygenase (HO)-1.Front Physiol. 2019 Feb 11;10:70. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00070. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30804804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress, Endothelial Dysfunction, and N-Acetylcysteine in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2024 Jun;40(16-18):968-989. doi: 10.1089/ars.2023.0524. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2024. PMID: 38497734 Review.
References
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–986. - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33) Lancet. 1998;352:837–853. - PubMed
-
- Ceriello A. New insights on oxidative stress and diabetic complications may lead to a "causal" antioxidant therapy. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:1589–1596. - PubMed
-
- Maritim AC, Sanders RA, Watkins JB., 3rd Diabetes, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: a review. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2003;17:24–38. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Chough E, Daley J, Oates P, Tornheim K, Ruderman NB, Keaney JF., Jr Hyperglycemia increases endothelial superoxide that impairs smooth muscle cell Na+-K+-ATPase activity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;282:C560–C566. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

