Lipidomic profiling in Crohn's disease: abnormalities in phosphatidylinositols, with preservation of ceramide, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine composition
- PMID: 22728312
- PMCID: PMC3778899
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.06.016
Lipidomic profiling in Crohn's disease: abnormalities in phosphatidylinositols, with preservation of ceramide, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine composition
Abstract
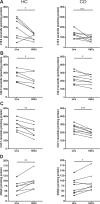
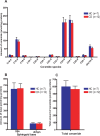
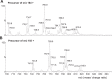
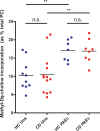
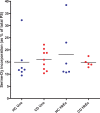
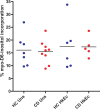
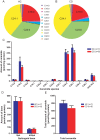
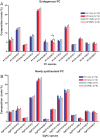
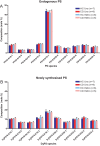
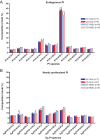
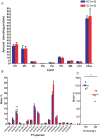
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory condition largely affecting the terminal ileum and large bowel. A contributing cause is the failure of an adequate acute inflammatory response as a result of impaired secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by macrophages. This defective secretion arises from aberrant vesicle trafficking, misdirecting the cytokines to lysosomal degradation. Aberrant intestinal permeability is also well-established in Crohn's disease. Both the disordered vesicle trafficking and increased bowel permeability could result from abnormal lipid composition. We thus measured the sphingo- and phospholipid composition of macrophages, using mass spectrometry and stable isotope labelling approaches. Stimulation of macrophages with heat-killed Escherichia coli resulted in three main changes; a significant reduction in the amount of individual ceramide species, an altered composition of phosphatidylcholine, and an increased rate of phosphatidylcholine synthesis in macrophages. These changes were observed in macrophages from both healthy control individuals and patients with Crohn's disease. The only difference detected between control and Crohn's disease macrophages was a reduced proportion of newly-synthesised phosphatidylinositol 16:0/18:1 over a defined time period. Shotgun lipidomics analysis of macroscopically non-inflamed ileal biopsies showed a significant decrease in this same lipid species with overall preservation of sphingolipid, phospholipid and cholesterol composition.
Crown Copyright © 2012. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Culture independent analysis of ileal mucosa reveals a selective increase in invasive Escherichia coli of novel phylogeny relative to depletion of Clostridiales in Crohn's disease involving the ileum.ISME J. 2007 Sep;1(5):403-18. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2007.52. Epub 2007 Jul 12. ISME J. 2007. PMID: 18043660
-
Crohn's disease-associated adherent invasive Escherichia coli modulate levels of microRNAs in intestinal epithelial cells to reduce autophagy.Gastroenterology. 2014 Feb;146(2):508-19. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.10.021. Epub 2013 Oct 19. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24148619
-
The ATG16L1-T300A allele impairs clearance of pathosymbionts in the inflamed ileal mucosa of Crohn's disease patients.Gut. 2015 Oct;64(10):1546-52. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307289. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Gut. 2015. PMID: 25253126
-
Quantitative Lipidomics in Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Oct 1;200(7):881-887. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201901-0086OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 31002528
-
Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli and Crohn's disease.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2007 Jan;23(1):16-20. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e3280105a38. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17133079 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome-wide association studies associated with Crohn's disease: challenges and perspectives.Cell Biosci. 2024 Feb 25;14(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01204-w. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38403629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ready-to-use therapeutic food with elevated n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid content, with or without fish oil, to treat severe acute malnutrition: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Med. 2015 Apr 23;13:93. doi: 10.1186/s12916-015-0315-6. BMC Med. 2015. PMID: 25902844 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The physical influence of inositides-a disproportionate effect?J Chem Biol. 2014 Jul 20;8(1):1-3. doi: 10.1007/s12154-014-0117-x. eCollection 2015 Jan. J Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 25584076 Free PMC article.
-
Global and Simultaneous Hypothesis Testing for High-Dimensional Logistic Regression Models.J Am Stat Assoc. 2021;116(534):984-998. doi: 10.1080/01621459.2019.1699421. Epub 2020 Jan 21. J Am Stat Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34421157 Free PMC article.
-
Further Insights into the Gut Microbiota of Cow's Milk Allergic Infants: Analysis of Microbial Functionality and Its Correlation with Three Fecal Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 25;24(11):9247. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119247. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amre D.K., D'Souza S., Morgan K., Seidman G., Lambrette P., Grimard G. Imbalances in dietary consumption of fatty acids, vegetables, and fruits are associated with risk for Crohn's disease in children. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2007;102:2016–2025. - PubMed
-
- Aozaki S. Decreased membrane fluidity in erythrocytes from patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterologia Japonica. 1989;24:246–254. - PubMed
-
- Balgoma D., Montero O., Balboa M.A., Balsinde J. Calcium-independent phospholipase A2-mediated formation of 1,2-diarachidonoyl-glycerophosphoinositol in monocytes. FEBS Journal. 2008;275:6180–6191. - PubMed
-
- Bielawski J., Pierce J.S., Snider J., Rembiesa B., Szulc Z.M., Bielawska A. Comprehensive quantitative analysis of bioactive sphingolipids by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2009;579:443–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

