The IkappaB kinase family phosphorylates the Parkinson's disease kinase LRRK2 at Ser935 and Ser910 during Toll-like receptor signaling
- PMID: 22723946
- PMCID: PMC3377608
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039132
The IkappaB kinase family phosphorylates the Parkinson's disease kinase LRRK2 at Ser935 and Ser910 during Toll-like receptor signaling
Abstract
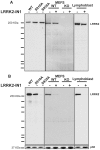
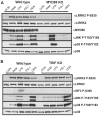
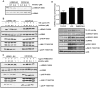
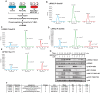
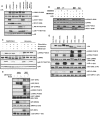
Mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) are strongly associated with late-onset autosomal dominant Parkinson's disease. LRRK2 is highly expressed in immune cells and recent work points towards a link between LRRK2 and innate immunity. Here we demonstrate that stimulation of the Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) pathway by MyD88-dependent agonists in bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) or RAW264.7 macrophages induces marked phosphorylation of LRRK2 at Ser910 and Ser935, the phosphorylation sites that regulate the binding of 14-3-3 to LRRK2. Phosphorylation of these residues is prevented by knock-out of MyD88 in BMDMs, but not the alternative TLR adaptor protein TRIF. Utilising both pharmacological inhibitors, including a new TAK1 inhibitor, NG25, and genetic models, we provide evidence that both the canonical (IKKα and IKKβ) and IKK-related (IKKε and TBK1) kinases mediate TLR agonist induced phosphorylation of LRRK2 in vivo. Moreover, all four IKK members directly phosphorylate LRRK2 at Ser910 and Ser935 in vitro. Consistent with previous work describing Ser910 and Ser935 as pharmacodynamic biomarkers of LRRK2 activity, we find that the TLR independent basal phosphorylation of LRRK2 at Ser910 and Ser935 is abolished following treatment of macrophages with LRRK2 kinase inhibitors. However, the increased phosphorylation of Ser910 and Ser935 induced by activation of the MyD88 pathway is insensitive to LRRK2 kinase inhibitors. Finally, employing LRRK2-deficient BMDMs, we present data indicating that LRRK2 does not play a major role in regulating the secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by activation of the MyD88 pathway. Our findings provide the first direct link between LRRK2 and the IKKs that mediate many immune responses. Further work is required to uncover the physiological roles that phosphorylation of LRRK2 by IKKs play in controlling macrophage biology and to determine how phosphorylation of LRRK2 by IKKs impacts upon the use of Ser910 and Ser935 as pharmacodynamic biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Measurement of LRRK2 and Ser910/935 phosphorylated LRRK2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from idiopathic Parkinson's disease patients.J Parkinsons Dis. 2013;3(2):145-52. doi: 10.3233/JPD-130174. J Parkinsons Dis. 2013. PMID: 23938344
-
The TRAF-associated protein TANK facilitates cross-talk within the IkappaB kinase family during Toll-like receptor signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Oct 11;108(41):17093-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1114194108. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21949249 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of LRRK2 kinase activity leads to dephosphorylation of Ser(910)/Ser(935), disruption of 14-3-3 binding and altered cytoplasmic localization.Biochem J. 2010 Sep 15;430(3):405-13. doi: 10.1042/BJ20100784. Biochem J. 2010. PMID: 20659021 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of LRRK2 cellular phosphorylation sites provides insight into LRRK2 biology.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Oct;40(5):1158-62. doi: 10.1042/BST20120137. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22988882 Review.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
Cited by
-
R1441G but not G2019S mutation enhances LRRK2 mediated Rab10 phosphorylation in human peripheral blood neutrophils.Acta Neuropathol. 2021 Sep;142(3):475-494. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02325-z. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Acta Neuropathol. 2021. PMID: 34125248 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's progression prediction using machine learning and serum cytokines.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2019 Jul 25;5:14. doi: 10.1038/s41531-019-0086-4. eCollection 2019. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2019. PMID: 31372494 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of Validating Antibodies and Small Compound Inhibitors Using Genetic Knockout Studies-T Cell Receptor-Induced CYLD Phosphorylation by IKKε/TBK1 as a Case Study.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Apr 10;6:40. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00040. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29755980 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and pharmacological evidence that G2019S LRRK2 confers a hyperkinetic phenotype, resistant to motor decline associated with aging.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Nov;71:62-73. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.07.013. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 25107341 Free PMC article.
-
Rab29 activation of the Parkinson's disease-associated LRRK2 kinase.EMBO J. 2018 Jan 4;37(1):1-18. doi: 10.15252/embj.201798099. Epub 2017 Dec 6. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 29212815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, Lichtner P, Farrer M, et al. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron. 2004;44:601–607. - PubMed
-
- Paisan-Ruiz C, Jain S, Evans EW, Gilks WP, Simon J, et al. Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson's disease. Neuron. 2004;44:595–600. - PubMed
-
- Mata IF, Wedemeyer WJ, Farrer MJ, Taylor JP, Gallo KA. LRRK2 in Parkinson's disease: protein domains and functional insights. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29:286–293. - PubMed
-
- Vancraenenbroeck R, Lobbestael E, Weeks SD, Strelkov SV, Baekelandt V, et al. Expression, purification and preliminary biochemical and structural characterization of the leucine rich repeat namesake domain of leucine rich repeat kinase 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1824:450–460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

