Tlx1/3 and Ptf1a control the expression of distinct sets of transmitter and peptide receptor genes in the developing dorsal spinal cord
- PMID: 22723691
- PMCID: PMC6620993
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6301-11.2012
Tlx1/3 and Ptf1a control the expression of distinct sets of transmitter and peptide receptor genes in the developing dorsal spinal cord
Abstract
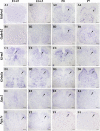
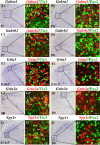
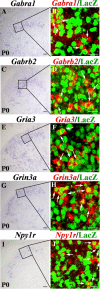
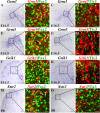
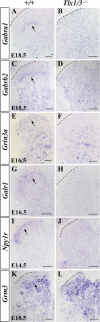
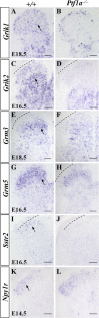
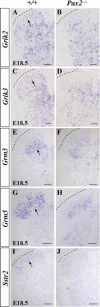
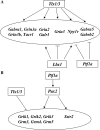
Establishing the pattern of expression of transmitters and peptides as well as their receptors in different neuronal types is crucial for understanding the circuitry in various regions of the brain. Previous studies have demonstrated that the transmitter and peptide phenotypes in mouse dorsal spinal cord neurons are determined by the transcription factors Tlx1/3 and Ptf1a. Here we show that these transcription factors also determine the expression of two distinct sets of transmitter and peptide receptor genes in this region. We have screened the expression of 78 receptor genes in the spinal dorsal horn by in situ hybridization. We found that receptor genes Gabra1, Gabra5, Gabrb2, Gria3, Grin3a, Grin3b, Galr1, and Npy1r were preferentially expressed in Tlx3-expressing glutamatergic neurons and their derivatives, and deletion of Tlx1 and Tlx3 resulted in the loss of expression of these receptor genes. Furthermore, we obtained genetic evidence that Tlx3 uses distinct pathways to control the expression of receptor genes. We also found that receptor genes Grm3, Grm4, Grm5, Grik1, Grik2, Grik3, and Sstr2 were mainly expressed in Pax2-expressing GABAergic neurons in the spinal dorsal horn, and their expression in this region was abolished or markedly reduced in Ptf1a and Pax2 deletion mutant mice. Together, our studies indicate that Tlx1/3 and Ptf1a, the key transcription factors for fate determination of glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in the dorsal spinal cord, are also responsible for controlling the expression of two distinct sets of transmitter and peptide receptor genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tlx3 and Tlx1 are post-mitotic selector genes determining glutamatergic over GABAergic cell fates.Nat Neurosci. 2004 May;7(5):510-7. doi: 10.1038/nn1221. Epub 2004 Apr 4. Nat Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15064766
-
Ptf1a determines GABAergic over glutamatergic neuronal cell fate in the spinal cord dorsal horn.Development. 2005 Dec;132(24):5461-9. doi: 10.1242/dev.02167. Epub 2005 Nov 16. Development. 2005. PMID: 16291784
-
Lbx1 and Tlx3 are opposing switches in determining GABAergic versus glutamatergic transmitter phenotypes.Nat Neurosci. 2005 Nov;8(11):1510-5. doi: 10.1038/nn1569. Epub 2005 Oct 23. Nat Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16234809
-
Lhx1 and Lhx5 maintain the inhibitory-neurotransmitter status of interneurons in the dorsal spinal cord.Development. 2007 Jan;134(2):357-66. doi: 10.1242/dev.02717. Epub 2006 Dec 13. Development. 2007. PMID: 17166926
-
Transcription factor Ptf1a in development, diseases and reprogramming.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Mar;76(5):921-940. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2972-z. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30470852 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Normal and abnormal coding of somatosensory stimuli causing pain.Nat Neurosci. 2014 Feb;17(2):183-91. doi: 10.1038/nn.3629. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Nat Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24473266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The homeodomain factor Gbx1 is required for locomotion and cell specification in the dorsal spinal cord.PeerJ. 2013 Aug 29;1:e142. doi: 10.7717/peerj.142. eCollection 2013. PeerJ. 2013. PMID: 24010020 Free PMC article.
-
Evx1 and Evx2 specify excitatory neurotransmitter fates and suppress inhibitory fates through a Pax2-independent mechanism.Neural Dev. 2016 Feb 19;11:5. doi: 10.1186/s13064-016-0059-9. Neural Dev. 2016. PMID: 26896392 Free PMC article.
-
Control of axon guidance and neurotransmitter phenotype of dB1 hindbrain interneurons by Lim-HD code.J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 11;35(6):2596-611. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2699-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25673852 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analyses of zebrafish V0v spinal interneurons and identification of transcriptional regulators downstream of Evx1 and Evx2 in these cells.Neural Dev. 2023 Nov 28;18(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13064-023-00176-w. Neural Dev. 2023. PMID: 38017520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almeida TA, Rojo J, Nieto PM, Pinto FM, Hernandez M, Martín JD, Candenas ML. Tachykinins and tachykinin receptors: structure and activity relationships. Curr Med Chem. 2004;11:2045–2081. - PubMed
-
- Barnard EA, Skolnick P, Olsen RW, Mohler H, Sieghart W, Biggio G, Braestrup C, Bateson AN, Langer SZ. International Union of Pharmacology. XV. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors: classification on the basis of subunit structure and receptor function. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:291–313. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MR, Balcar VJ. Forty years of amino acid transmission in the brain. Neurochem Int. 1999;35:269–280. - PubMed
-
- Bettler B, Tiao JY. Molecular diversity, trafficking and subcellular localization of GABAB receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;110:533–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
