Autoregulation of microRNA biogenesis by let-7 and Argonaute
- PMID: 22722835
- PMCID: PMC3387326
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11134
Autoregulation of microRNA biogenesis by let-7 and Argonaute
Abstract
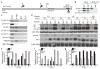
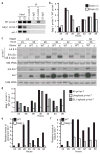
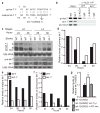
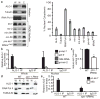
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) comprise a large family of small RNA molecules that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression in many biological pathways. Most miRNAs are derived from long primary transcripts that undergo processing by Drosha to produce ~65-nucleotide precursors that are then cleaved by Dicer, resulting in the mature 22-nucleotide forms. Serving as guides in Argonaute protein complexes, mature miRNAs use imperfect base pairing to recognize sequences in messenger RNA transcripts, leading to translational repression and destabilization of the target messenger RNAs. Here we show that the miRNA complex also targets and regulates non-coding RNAs that serve as substrates for the miRNA-processing pathway. We found that the Argonaute protein in Caenorhabditis elegans, ALG-1, binds to a specific site at the 3′ end of let-7 miRNA primary transcripts and promotes downstream processing events. This interaction is mediated by mature let-7 miRNA through a conserved complementary site in its own primary transcript, thus creating a positive-feedback loop. We further show that ALG-1 associates with let-7 primary transcripts in nuclear fractions. Argonaute also binds let-7 primary transcripts in human cells, demonstrating that the miRNA pathway targets non-coding RNAs in addition to protein-coding messenger RNAs across species. Moreover, our studies in C. elegans reveal a novel role for Argonaute in promoting biogenesis of a targeted transcript, expanding the functions of the miRNA pathway in gene regulation. This discovery of autoregulation of let-7 biogenesis establishes a new mechanism for controlling miRNA expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
MicroRNAs micromanage themselves.Circ Res. 2012 Nov 9;111(11):1395-7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.281014. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 23139285 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Splicing remodels the let-7 primary microRNA to facilitate Drosha processing in Caenorhabditis elegans.RNA. 2015 Aug;21(8):1396-403. doi: 10.1261/rna.052118.115. Epub 2015 Jun 16. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26081559 Free PMC article.
-
LIN-28 co-transcriptionally binds primary let-7 to regulate miRNA maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Mar;18(3):302-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1986. Epub 2011 Feb 6. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21297634 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling neurodevelopmental disorder-associated human AGO1 mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans Argonaute alg-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Mar 5;121(10):e2308255121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2308255121. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38412125 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of microRNA expression and function.Methods Cell Biol. 2011;106:219-252. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-544172-8.00008-6. Methods Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 22118279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis and regulation of the let-7 miRNAs and their functional implications.Protein Cell. 2016 Feb;7(2):100-13. doi: 10.1007/s13238-015-0212-y. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Protein Cell. 2016. PMID: 26399619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LIN28 binds messenger RNAs at GGAGA motifs and regulates splicing factor abundance.Mol Cell. 2012 Oct 26;48(2):195-206. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.08.004. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22959275 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear microRNAs and their unconventional role in regulating non-coding RNAs.Protein Cell. 2013 May;4(5):325-30. doi: 10.1007/s13238-013-3001-5. Epub 2013 Apr 13. Protein Cell. 2013. PMID: 23584808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the functional explorations of nuclear microRNAs.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 22;14:1097491. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1097491. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36911728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRBaseMiner, a tool for investigating miRBase content.RNA Biol. 2019 Nov;16(11):1534-1546. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1637680. Epub 2019 Aug 12. RNA Biol. 2019. PMID: 31251108 Free PMC article.
-
Lin28: an emerging important oncogene connecting several aspects of cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Mar;37(3):2841-8. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4759-2. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26762415 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

