Foot-and-mouth disease virus 3C protease cleaves NEMO to impair innate immune signaling
- PMID: 22718831
- PMCID: PMC3416110
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00722-12
Foot-and-mouth disease virus 3C protease cleaves NEMO to impair innate immune signaling
Abstract
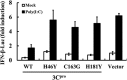
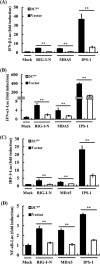
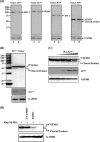
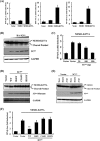
Foot-and-mouth disease is a highly contagious viral illness of wild and domestic cloven-hoofed animals. The causative agent, foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV), replicates rapidly, efficiently disseminating within the infected host and being passed on to susceptible animals via direct contact or the aerosol route. To survive in the host, FMDV has evolved to block the host interferon (IFN) response. Previously, we and others demonstrated that the leader proteinase (L(pro)) of FMDV is an IFN antagonist. Here, we report that another FMDV-encoded proteinase, 3C(pro), also inhibits IFN-α/β response and the expression of IFN-stimulated genes. Acting in a proteasome- and caspase-independent manner, the 3C(pro) of FMDV proteolytically cleaved nuclear transcription factor kappa B (NF-κB) essential modulator (NEMO), a bridging adaptor protein essential for activating both NF-κB and interferon-regulatory factor signaling pathways. 3C(pro) specifically targeted NEMO at the Gln 383 residue, cleaving off the C-terminal zinc finger domain from the protein. This cleavage impaired the ability of NEMO to activate downstream IFN production and to act as a signaling adaptor of the RIG-I/MDA5 pathway. Mutations specifically disrupting the cysteine protease activity of 3C(pro) abrogated NEMO cleavage and the inhibition of IFN induction. Collectively, our data identify NEMO as a substrate for FMDV 3C(pro) and reveal a novel mechanism evolved by a picornavirus to counteract innate immune signaling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Antagonizes NOD2-Mediated Antiviral Effects by Inhibiting NOD2 Protein Expression.J Virol. 2019 May 15;93(11):e00124-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00124-19. Print 2019 Jun 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30894473 Free PMC article.
-
3Cpro of foot-and-mouth disease virus antagonizes the interferon signaling pathway by blocking STAT1/STAT2 nuclear translocation.J Virol. 2014 May;88(9):4908-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03668-13. Epub 2014 Feb 19. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24554650 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus 3C-Like Protease Regulates Its Interferon Antagonism by Cleaving NEMO.J Virol. 2015 Dec 9;90(4):2090-101. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02514-15. Print 2016 Feb 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26656704 Free PMC article.
-
Evading the host immune response: how foot-and-mouth disease virus has become an effective pathogen.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008 Jun;53(1):8-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2008.00409.x. Epub 2008 Apr 8. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18400012 Review.
-
Interplay of foot and mouth disease virus with cell-mediated and humoral immunity of host.Rev Med Virol. 2018 Mar;28(2). doi: 10.1002/rmv.1966. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Rev Med Virol. 2018. PMID: 29282795 Review.
Cited by
-
Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus: An Updated Overview of Virus Epidemiology, Virulence Variation Patterns and Virus-Host Interactions.Viruses. 2022 Nov 2;14(11):2434. doi: 10.3390/v14112434. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36366532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Viroporin 2B Antagonizes RIG-I-Mediated Antiviral Effects by Inhibition of Its Protein Expression.J Virol. 2016 Nov 28;90(24):11106-11121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01310-16. Print 2016 Dec 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27707918 Free PMC article.
-
3Cpro of FMDV inhibits type II interferon-stimulated JAK-STAT signaling pathway by blocking STAT1 nuclear translocation.Virol Sin. 2023 Jun;38(3):387-397. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2023.03.003. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Virol Sin. 2023. PMID: 36921803 Free PMC article.
-
Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus Nsp5 Inhibits Type I Interferon Production by Cleaving NEMO at Multiple Sites.Viruses. 2019 Dec 30;12(1):43. doi: 10.3390/v12010043. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31905881 Free PMC article.
-
Induction and suppression of innate antiviral responses by picornaviruses.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Oct;25(5):577-85. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 25086453 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

