l-Tetrahydropalmatine, an active component of Corydalis yanhusuo W.T. Wang, protects against myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats
- PMID: 22715398
- PMCID: PMC3371051
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038627
l-Tetrahydropalmatine, an active component of Corydalis yanhusuo W.T. Wang, protects against myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats
Abstract
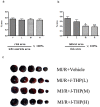
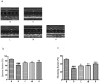
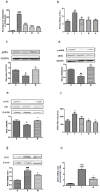
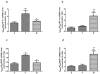
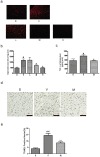
l-Tetrahydropalmatine (l-THP) is an active ingredients of Corydalis yanhusuo W.T. Wang, which protects against acute global cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury. In this study, we show that l-THP is cardioprotective in myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury and examined the mechanism. Rats were treated with l-THP (0, 10, 20, 40 mg/kg b.w.) for 20 min before occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery and subjected to myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion (30 min/6 h). Compared with vehicle-treated animals, the infarct area/risk area (IA/RA) of l-THP (20, 40 mg/kg b.w.) treated rats was reduced, whilst l-THP (10 mg/kg b.w.) had no significant effect. Cardiac function was improved in l-THP-treated rats whilst plasma creatine kinase activity declined. Following treatment with l-THP (20 mg/kg b.w.), subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p85, serine(473) phosphorylation of Akt and serine(1177) phosphorylation of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) increased in myocardium, whilst expression of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) decreased. However, the expression of HIF-1α and VEGF were increased in I(30 min)R(6 h), but decreased to normal level in I(30 min)R(24 h), while treatment with l-THP (20 mg/kg b.w.) enhanced the levels of these two genes in I(30 min)R(24 h). Production of NO in myocardium and plasma, activity of myeloperoxidase (MPO) in plasma and the expression of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in myocardium were decreased by l-THP. TUNEL assay revealed that l-THP (20 mg/kg b.w.) reduced apoptosis in myocardium. Thus, we show that l-THP activates the PI3K/Akt/eNOS/NO pathway and increases expression of HIF-1α and VEGF, whilst depressing iNOS-derived NO production in myocardium. This effect may decrease the accumulation of inflammatory factors, including TNF-α and MPO, and lessen the extent of apoptosis, therefore contributing to the cardioprotective effects of l-THP in myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

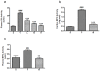
Similar articles
-
Adiponectin protects against myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury via AMP-activated protein kinase, Akt, and nitric oxide.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Apr 1;78(1):116-22. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn017. Epub 2008 Jan 25. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18222959
-
PPAR-alpha activation protects the type 2 diabetic myocardium against ischemia-reperfusion injury: involvement of the PI3-Kinase/Akt and NO pathway.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Mar;296(3):H719-27. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00394.2008. Epub 2009 Jan 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19151258
-
Protective effect of ligustrazine against myocardial ischaemia reperfusion in rats: the role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012 Jan;39(1):20-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05628.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22004361
-
Advances in phytochemical and modern pharmacological research of Rhizoma Corydalis.Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):265-275. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1741651. Pharm Biol. 2020. PMID: 32223481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of cardioprotection by isoflurane against I/R injury.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013 Jan 1;18(1):387-93. doi: 10.2741/4109. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013. PMID: 23276931 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating Full-Length and Second-Generation Transcriptomics to Reveal Differentially Expressed Genes Associated with the Development of Corydalis yanhusuo Tuber.Life (Basel). 2023 Nov 14;13(11):2207. doi: 10.3390/life13112207. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004347 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Pharmacological Mechanisms of SheXiang XinTongNing Against Coronary Heart Disease Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Evaluation.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 14;12:698981. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.698981. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34335263 Free PMC article.
-
Levo-tetrahydropalmatine attenuates mouse blood-brain barrier injury induced by focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion: Involvement of Src kinase.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 10;5:11155. doi: 10.1038/srep11155. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26059793 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of N-acetylcysteine activated carbon release microcapsule on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Feb;15(2):1809-1818. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5653. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29434769 Free PMC article.
-
L-tetrahydropalmatine ameliorates development of anxiety and depression-related symptoms induced by single prolonged stress in rats.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2014 May;22(3):213-22. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2014.032. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2014. PMID: 25009702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Griendling KK, Alexander RW. Oxidative stress and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 1997;96:3264–3265. - PubMed
-
- McCord JM. Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med. 1985;312:159–163. - PubMed
-
- Dinerman JL, Lowenstein CJ, Snyder SH. Molecular mechanisms of nitric oxide regulation. Potential relevance to cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 1993;73:217–222. - PubMed
-
- Radomski MW, Palmer RM, Moncada S. Endogenous nitric oxide inhibits human platelet adhesion to vascular endothelium. Lancet. 1987;2:1057–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

