Cellular basis of tissue regeneration by omentum
- PMID: 22701632
- PMCID: PMC3368844
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038368
Cellular basis of tissue regeneration by omentum
Abstract
The omentum is a sheet-like tissue attached to the greater curvature of the stomach and contains secondary lymphoid organs called milky spots. The omentum has been used for its healing potential for over 100 years by transposing the omental pedicle to injured organs (omental transposition), but the mechanism by which omentum helps the healing process of damaged tissues is not well understood. Omental transposition promotes expansion of pancreatic islets, hepatocytes, embryonic kidney, and neurons. Omental cells (OCs) can be activated by foreign bodies in vivo. Once activated, they become a rich source for growth factors and express pluripotent stem cell markers. Moreover, OCs become engrafted in injured tissues suggesting that they might function as stem cells.Omentum consists of a variety of phenotypically and functionally distinctive cells. To understand the mechanism of tissue repair support by the omentum in more detail, we analyzed the cell subsets derived from the omentum on immune and inflammatory responses. Our data demonstrate that the omentum contains at least two groups of cells that support tissue repair, immunomodulatory myeloid derived suppressor cells and omnipotent stem cells that are indistinguishable from mesenchymal stem cells. Based on these data, we propose that the omentum is a designated organ for tissue repair and healing in response to foreign invasion and tissue damage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

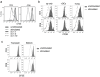

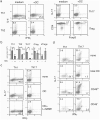
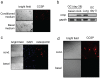
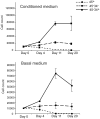
Similar articles
-
Activated omentum becomes rich in factors that promote healing and tissue regeneration.Cell Tissue Res. 2007 Jun;328(3):487-97. doi: 10.1007/s00441-006-0356-4. Epub 2007 Feb 14. Cell Tissue Res. 2007. PMID: 17468892
-
Morpho-physiological function and role of omental milky spots as omentum-associated lymphoid tissue (OALT) in the peritoneal cavity.Lymphology. 1993 Jun;26(2):90-101. Lymphology. 1993. PMID: 8355522 Review.
-
Culture of omentum-induced regenerating liver yielded hepatocyte-committed stem cells.Transl Res. 2010 Dec;156(6):358-68. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2010.09.002. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Transl Res. 2010. PMID: 21078497
-
Omental grafting: a cell-based therapy for blood vessel repair.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013 Jun;7(6):421-33. doi: 10.1002/term.528. Epub 2012 Feb 8. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013. PMID: 22318999 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Regeneration: Endogenous and Exogenous Stem Cell Mediated Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jan 19;17(1):128. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010128. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26797607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the effect of subcutaneous injection of omental-derived cells on the healing of third degree burns in rats: a preliminary study.Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2018 Mar 31;31(1):59-64. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2018. PMID: 30174575 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of activated omental extract on nuclear and cytoplasmic in vitro maturation of rat oocytes.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2017 Dec;20(12):1345-1353. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2017.9622. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29238470 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic omentectomy in gynecologic oncology: surgical anatomy, indications, and a technical approach.J Robot Surg. 2023 Aug;17(4):1381-1391. doi: 10.1007/s11701-022-01519-1. Epub 2023 Jan 17. J Robot Surg. 2023. PMID: 36648633 Review.
-
Bioengineered omental transplant site promotes pancreatic islet allografts survival in non-human primates.Cell Rep Med. 2023 Mar 21;4(3):100959. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.100959. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Cell Rep Med. 2023. PMID: 36863336 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of butyric acid with autogenous omental graft on healing of experimental Achilles tendon injury in rabbits.Iran J Vet Res. 2015 Winter;16(1):100-4. Iran J Vet Res. 2015. PMID: 27175160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cannaday JE. Some uses of undetached omentum in surgery. Am J Surg. 1948;76:502–505. - PubMed
-
- Vineberg AM, Kato Y, Pirozynski WJ. Experimental revascularization of the entire heart. Evaluation of epicardiectomy, omental graft, and/or implantation of the internal mammary artery in preventing myocardial necrosis and death of the animal. Am Heart J. 1966;72:79–93. - PubMed
-
- Vernik J, Singh AK. Omentum: power to heal and regenerate. Int J Artif Organs. 2007;30:95–99. - PubMed
-
- Collins D, Hogan AM, O'Shea D, Winter DC. The omentum: anatomical, metabolic, and surgical aspects. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009;13:1138–1146. - PubMed
-
- Liebermann-Meffert D. The greater omentum. Anatomy, embryology, and surgical applications. Surg Clin North Am 80: 275–293, 2000;xii - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

