Lck, Membrane Microdomains, and TCR Triggering Machinery: Defining the New Rules of Engagement
- PMID: 22701458
- PMCID: PMC3372939
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00155
Lck, Membrane Microdomains, and TCR Triggering Machinery: Defining the New Rules of Engagement
Abstract
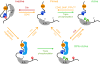
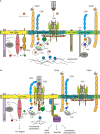
In spite of a comprehensive understanding of the schematics of T cell receptor (TCR) signaling, the mechanisms regulating compartmentalization of signaling molecules, their transient interactions, and rearrangement of membrane structures initiated upon TCR engagement remain an outstanding problem. These gaps in our knowledge are exemplified by recent data demonstrating that TCR triggering is largely dependent on a preactivated pool of Lck concentrated in T cells in a specific type of membrane microdomains. Our current model posits that in resting T cells all critical components of TCR triggering machinery including TCR/CD3, Lck, Fyn, CD45, PAG, and LAT are associated with distinct types of lipid-based microdomains which represent the smallest structural and functional units of membrane confinement able to negatively control enzymatic activities and substrate availability that is required for the initiation of TCR signaling. In addition, the microdomains based segregation spatially limits the interaction of components of TCR triggering machinery prior to the onset of TCR signaling and allows their rapid communication and signal amplification after TCR engagement, via the process of their coalescence. Microdomains mediated compartmentalization thus represents an essential membrane organizing principle in resting T cells. The integration of these structural and functional aspects of signaling into a unified model of TCR triggering will require a deeper understanding of membrane biology, novel interdisciplinary approaches and the generation of specific reagents. We believe that the fully integrated model of TCR signaling must be based on membrane structural network which provides a proper environment for regulatory processes controlling TCR triggering.
Keywords: Fyn; Lck; TCR triggering; compartmentalization; heavy and light DRMs; membrane microdomains; spatio-temporal regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting of CD45 protein tyrosine phosphatase activity to lipid microdomains on the T cell surface inhibits TCR signaling.Eur J Immunol. 2002 Sep;32(9):2578-87. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200209)32:9<2578::AID-IMMU2578>3.0.CO;2-3. Eur J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12207342
-
Enrichment of lck in lipid rafts regulates colocalized fyn activation and the initiation of proximal signals through TCR alpha beta.J Immunol. 2004 Apr 1;172(7):4266-74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.7.4266. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15034040
-
Lipid rafts: resolution of the "fyn problem"?Mol Immunol. 2004 Jul;41(6-7):645-56. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.04.011. Mol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15220001 Review.
-
A specific type of membrane microdomains is involved in the maintenance and translocation of kinase active Lck to lipid rafts.Immunol Lett. 2012 Feb 29;142(1-2):64-74. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2012.01.001. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Immunol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22281390
-
Lipid rafts: cell surface platforms for T cell signaling.Biol Res. 2002;35(2):127-31. doi: 10.4067/s0716-97602002000200003. Biol Res. 2002. PMID: 12415729 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of FRET and sequencing to engineer kinase biosensors from mammalian cell libraries.Nat Commun. 2021 Aug 19;12(1):5031. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25323-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34413312 Free PMC article.
-
TCR Signaling: Mechanisms of Initiation and Propagation.Trends Biochem Sci. 2018 Feb;43(2):108-123. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2017.11.008. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Trends Biochem Sci. 2018. PMID: 29269020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel role for an old target: CD45 for breast cancer immunotherapy.Oncoimmunology. 2021 May 25;10(1):1929725. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1929725. Oncoimmunology. 2021. PMID: 34104545 Free PMC article.
-
Lck Function and Modulation: Immune Cytotoxic Response and Tumor Treatment More Than a Simple Event.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 24;16(15):2630. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152630. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A biophysical perspective on receptor-mediated virus entry with a focus on HIV.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Jun 1;1862(6):183158. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.183158. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 31863725 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

