Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus G-protein-coupled receptor prevents AU-rich-element-mediated mRNA decay
- PMID: 22696654
- PMCID: PMC3421767
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00597-12
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus G-protein-coupled receptor prevents AU-rich-element-mediated mRNA decay
Abstract
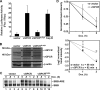
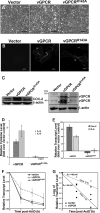
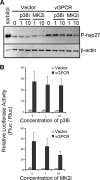
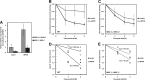
During lytic Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) infection, host gene expression is severely restricted by a process of global mRNA degradation known as host shutoff, which rededicates translational machinery to the expression of viral proteins. A subset of host mRNAs is spared from shutoff, and a number of these contain cis-acting AU-rich elements (AREs) in their 3' untranslated regions. AREs are found in labile mRNAs encoding cytokines, growth factors, and proto-oncogenes. Activation of the p38/MK2 signal transduction pathway reverses constitutive decay of ARE-mRNAs, resulting in increased protein production. The viral G-protein-coupled receptor (vGPCR) is thought to play an important role in promoting the secretion of angiogenic molecules from KSHV-infected cells during lytic replication, but to date it has not been clear how vGPCR circumvents host shutoff. Here, we demonstrate that vGPCR activates the p38/MK2 pathway and stabilizes ARE-mRNAs, augmenting the levels of their protein products. Using MK2-deficient cells, we demonstrate that MK2 is essential for maximal vGPCR-mediated ARE-mRNA stabilization. ARE-mRNAs are normally delivered to cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granules known as processing bodies (PBs) for translational silencing and decay. We demonstrate that PB formation is prevented during KSHV lytic replication or in response to vGPCR-mediated activation of RhoA subfamily GTPases. Together, these data show for the first time that vGPCR impacts gene expression at the posttranscriptional level, coordinating an attack on the host mRNA degradation machinery. By suppressing ARE-mRNA turnover, vGPCR may facilitate escape of certain target mRNAs from host shutoff and allow secretion of angiogenic factors from lytically infected cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Viral activation of MK2-hsp27-p115RhoGEF-RhoA signaling axis causes cytoskeletal rearrangements, p-body disruption and ARE-mRNA stabilization.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Jan 8;11(1):e1004597. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004597. eCollection 2015 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25569678 Free PMC article.
-
The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus G protein-coupled receptor has broad signaling effects in primary effusion lymphoma cells.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(1):57-67. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.1.57-67.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12477810 Free PMC article.
-
The kaposin B protein of KSHV activates the p38/MK2 pathway and stabilizes cytokine mRNAs.Science. 2005 Feb 4;307(5710):739-41. doi: 10.1126/science.1105779. Science. 2005. PMID: 15692053
-
Viral activation of stress-regulated Rho-GTPase signaling pathway disrupts sites of mRNA degradation to influence cellular gene expression.Small GTPases. 2015 Oct 2;6(4):178-85. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2015.1093068. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Small GTPases. 2015. PMID: 26480288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Initiation of angiogenic Kaposi's sarcoma lesions.Cancer Cell. 2003 Jan;3(1):1-3. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00002-3. Cancer Cell. 2003. PMID: 12559168 Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies for Success. Viral Infections and Membraneless Organelles.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Oct 11;9:336. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00336. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31681621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KSHV G-protein coupled receptor vGPCR oncogenic signaling upregulation of Cyclooxygenase-2 expression mediates angiogenesis and tumorigenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Oct 15;16(10):e1009006. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009006. eCollection 2020 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 33057440 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Granules in Antiviral Innate Immunity: A Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Journey.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jan 5;12:794431. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.794431. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35069491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral Manipulation of a Mechanoresponsive Signaling Axis Disassembles Processing Bodies.Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Oct 26;41(11):e0039921. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00399-21. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34516278 Free PMC article.
-
Human coronaviruses disassemble processing bodies.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Aug 23;18(8):e1010724. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010724. eCollection 2022 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35998203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. 2008. Stress granules: the Tao of RNA triage. Trends Biochem. Sci. 33:141–150 - PubMed
-
- Arvanitakis L, Geras-Raaka E, Varma A, Gershengorn MC, Cesarman E. 1997. Human herpesvirus KSHV encodes a constitutively active G-protein-coupled receptor linked to cell proliferation. Nature 385:347–350 - PubMed
-
- Bais C, et al. 1998. G-protein-coupled receptor of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is a viral oncogene and angiogenesis activator. Nature 391:86–89 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

