Characterization of infectivity-enhanced conditionally replicating adenovectors for prostate cancer radiovirotherapy
- PMID: 22694073
- PMCID: PMC3440023
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2012.047
Characterization of infectivity-enhanced conditionally replicating adenovectors for prostate cancer radiovirotherapy
Abstract
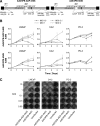
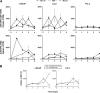
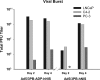
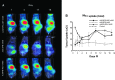
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second most commonly diagnosed and sixth leading cause of cancer death in American men and one for which no curative therapy exists after metastasis. To meet this need for novel therapies, our laboratory has previously generated conditionally replicating adenovirus (CRAd) vectors expressing the sodium iodide symporter (hNIS). This virus transduced PCa cells and induced functional NIS expression, allowing for noninvasive tumor imaging and combination therapy with radioiodide, referred to as radiovirotherapy. We have now generated two new modified vectors to further improve efficacy. Ad5/3PB-ADP-hNIS and Ad5/3PB-hNIS include a hybrid Ad5/3 fiber knob to improve transduction efficiency, and express NIS from the endogenous major late promoter to restrict NIS expression to target cells. Additionally, Ad5/3PB-ADP-hNIS includes the adenovirus death protein (ADP), which hastens the release of viral particles after assembly. These two vectors specifically induce radioisotope uptake, cytopathic effect, and viral replication in androgen receptor-expressing PCa cell lines with Ad5/3PB-ADP-hNIS showing earlier (131)I uptake and cytolysis at low multiplicity of infection. SPECT-CT imaging of xenograft tumors infected with Ad5/3PB-hNIS showed steady uptake, whereas infection with Ad5/3PB-ADP-hNIS led to increasing uptake, indicating viral spread. Radiovirotherapy of xenograft LNCaP tumors with Ad5/3PB-ADP-hNIS showed the most significant survival extension versus control tumors (p=0.001), but the benefit of radiovirotherapy was not statistically significant compared with virotherapy alone in this model. These results show the potential of Ad5/3PB-ADP-hNIS as a vector for treatment of prostate cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of increased viral replication and infectivity enhancement on radioiodide uptake and oncolytic activity of adenovirus vectors expressing the sodium iodide symporter.Cancer Gene Ther. 2013 Mar;20(3):195-200. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2013.4. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013. PMID: 23412431
-
A probasin promoter, conditionally replicating adenovirus that expresses the sodium iodide symporter (NIS) for radiovirotherapy of prostate cancer.Gene Ther. 2010 Nov;17(11):1325-32. doi: 10.1038/gt.2010.63. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Gene Ther. 2010. PMID: 20428214 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic image-guided liver cancer radiovirotherapy using dendrimer-coated adenovirus encoding the sodium iodide symporter as theranostic gene.J Nucl Med. 2013 Aug;54(8):1450-7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.115493. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Nucl Med. 2013. PMID: 23843567
-
Gene therapy with sodium/iodide symporter in hepatocarcinoma.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001;109(1):60-2. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-11010. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001. PMID: 11573143 Review.
-
Developing an effective gene therapy for prostate cancer: New technologies with potential to translate from the laboratory into the clinic.Discov Med. 2011 Jan;11(56):46-56. Discov Med. 2011. PMID: 21276410 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An oncolytic adenovirus 11p vector expressing adenovirus death protein in the E1 region showed significant apoptosis and tumour-killing ability in metastatic prostate cells.Oncotarget. 2019 Mar 8;10(20):1957-1974. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26754. eCollection 2019 Mar 8. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 30956777 Free PMC article.
-
The use of the NIS reporter gene for optimizing oncolytic virotherapy.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016;16(1):15-32. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2016.1100162. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26457362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer imaging and therapy utilizing a novel NIS-expressing adenovirus: The role of adenovirus death protein deletion.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021 Mar 5;20:659-668. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.03.002. eCollection 2021 Mar 26. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021. PMID: 33816784 Free PMC article.
-
Progresses towards safe and efficient gene therapy vectors.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 13;6(31):30675-703. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5169. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26362400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncolytic Adenovirus for the Targeting of Paclitaxel-Resistant Breast Cancer Stem Cells.Viruses. 2024 Apr 5;16(4):567. doi: 10.3390/v16040567. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38675909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andriani F. Nan B. Yu J., et al. Use of the probasin promoter ARR2PB to express Bax in androgen receptor-positive prostate cancer cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001;93:1314–1324. - PubMed
-
- Barton K.N. Paielli D. Zhang Y., et al. Second-generation replication-competent oncolytic adenovirus armed with improved suicide genes and ADP gene demonstrates greater efficacy without increased toxicity. Mol. Ther. 2006;13:347–356. - PubMed
-
- Cho J.-Y. Xing S. Liu X., et al. Expression and activity of human Na+/I− symporter in human glioma cells by adenovirus mediated gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2000;7:740–749. - PubMed
-
- Crnalic S. Hörnberg E. Wikström P., et al. Nuclear androgen receptor staining in bone metastases is related to a poor outcome in prostate cancer patients. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2010;17:885–895. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

