Akt1 inhibits homologous recombination in Brca1-deficient cells by blocking the Chk1-Rad51 pathway
- PMID: 22665067
- PMCID: PMC3700338
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.211
Akt1 inhibits homologous recombination in Brca1-deficient cells by blocking the Chk1-Rad51 pathway
Abstract
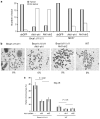
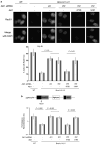
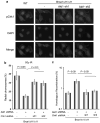
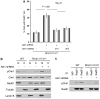
Brca1 deficiency leads to the development of breast cancer. We previously found that Brca1 deficiency activates the Akt oncogenic pathway. Reduced expression of Brca1 was highly correlated with increased activated Akt in human breast cancer samples. Furthermore, activation of Akt1 was involved in Brca1-deficiency-mediated tumorigenesis in mice. Defective homologous recombination (HR) is thought to be a major contributor to tumorigenesis in Brca1 deficiency. Here, we show that Akt1 promotes chromosome instability in Brca1-deficent cells. DNA breaks in Brca1-deficent cells are aberrantly joined into complex chromosome rearrangements by a process dependent on Akt1. Depletion of Akt1 increases HR in Brca1-mutant cells, which is rescued by expression of wild-type, but not mutant Akt1 with deletion of Brca1-binding domain. Mechanistically, activated Akt1 in Brca1-deficient cells impairs Chk1 nuclear localization and subsequently disrupts interaction of Chk1 and Rad51 leading to HR defects. Our results indicate that Brca1 deficiency might activate Akt1 contributing to tumorigenesis through regulation of the Chk1-Rad51 signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AKT1 inhibits homologous recombination by inducing cytoplasmic retention of BRCA1 and RAD51.Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 15;68(22):9404-12. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0861. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19010915
-
Targeting the Akt/mTOR pathway in Brca1-deficient cancers.Oncogene. 2011 May 26;30(21):2443-50. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.603. Epub 2011 Jan 17. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21242970 Free PMC article.
-
53BP1 inhibits homologous recombination in Brca1-deficient cells by blocking resection of DNA breaks.Cell. 2010 Apr 16;141(2):243-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.012. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20362325 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic exploitation of tumor cell defects in homologous recombination.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008 May;8(4):448-60. doi: 10.2174/187152008784220267. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18473729 Review.
-
Homologous recombination and human health: the roles of BRCA1, BRCA2, and associated proteins.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Apr 1;7(4):a016600. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016600. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 25833843 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of AKT signaling in DNA repair and clinical response to cancer therapy.Neuro Oncol. 2014 Oct;16(10):1313-23. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou058. Epub 2014 May 7. Neuro Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24811392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 confers PARP inhibitor resistance in BRCA1-deficient cancers.Oncotarget. 2014 May 30;5(10):3375-85. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1952. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24831086 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the AKT pathway: Repositioning HIV protease inhibitors as radiosensitizers.Indian J Med Res. 2016 Feb;143(2):145-59. doi: 10.4103/0971-5916.180201. Indian J Med Res. 2016. PMID: 27121513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akt1 Stimulates Homologous Recombination Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in a Rad51-Dependent Manner.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 20;18(11):2473. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112473. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29156644 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of AKT-Signaling Sensitizes Soft Tissue Sarcomas (STS) and Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) to Doxorubicin via Targeting of Homology-Mediated DNA Repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 22;21(22):8842. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228842. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33266502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miki Y, Swensen J, Shattuck-Eidens D, Futreal PA, Harshman K, Tavtigian S, et al. A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science. 1994;266:66–71. - PubMed
-
- Yu X, Chini CC, He M, Mer G, Chen J. The BRCT domain is a phospho-protein binding domain. Science. 2003;302:639–642. - PubMed
-
- Manke IA, Lowery DM, Nguyen A, Yaffe MB. BRCT repeats as phosphopeptide-binding modules involved in protein targeting. Science. 2003;302:636–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

