Characterization of a series of 4-aminoquinolines that stimulate caspase-7 mediated cleavage of TDP-43 and inhibit its function
- PMID: 22659571
- PMCID: PMC3402613
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.05.020
Characterization of a series of 4-aminoquinolines that stimulate caspase-7 mediated cleavage of TDP-43 and inhibit its function
Abstract
Dysfunction of the heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein TAR DNA binding protein 43 (TDP-43) is associated with neurodegeneration in diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD). Here we examine the effects of a series of 4-aminoquinolines with affinity for TDP-43 upon caspase-7-induced cleavage of TDP-43 and TDP-43 cellular function. These compounds were mixed inhibitors of biotinylated TG6 binding to TDP-43, binding to both free and occupied TDP-43. Incubation of TDP-43 and caspase-7 in the presence of these compounds stimulated caspase-7 mediated cleavage of TDP-43. This effect was antagonized by the oligonucleotide TG12, prevented by denaturing TDP-43, and exhibited a similar relation of structure to function as for the displacement of bt-TG6 binding to TDP-43. In addition, the compounds did not affect caspase-7 enzyme activity. In human neuroglioma H4 cells, these compounds lowered levels of TDP-43 and increased TDP-43 C-terminal fragments via a caspase-dependent mechanism. Subsequent experiments demonstrated that this was due to induction of caspases 3 and 7 leading to increased PARP cleavage in H4 cells with similar rank order of the potency among the compounds tests for displacement of bt-TG6 binding. Exposure to these compounds also reduced HDAC-6, ATG-7, and increased LC3B, consistent with the effects of TDP-43 siRNA described by other investigators. These data suggest that such compounds may be useful biochemical probes to further understand both the normal and pathological functions of TDP-43, and its cleavage and metabolism promoted by caspases.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
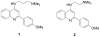



Similar articles
-
Ubiquilin-2 (UBQLN2) binds with high affinity to the C-terminal region of TDP-43 and modulates TDP-43 levels in H4 cells: characterization of inhibition by nucleic acids and 4-aminoquinolines.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun;1834(6):964-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.03.020. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23541532 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a novel nonradiometric assay for nucleic acid binding to TDP-43 suitable for high-throughput screening using AlphaScreen technology.J Biomol Screen. 2010 Oct;15(9):1099-106. doi: 10.1177/1087057110382778. Epub 2010 Sep 20. J Biomol Screen. 2010. PMID: 20855563 Free PMC article.
-
Progranulin mediates caspase-dependent cleavage of TAR DNA binding protein-43.J Neurosci. 2007 Sep 26;27(39):10530-4. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3421-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17898224 Free PMC article.
-
How do the RNA-binding proteins TDP-43 and FUS relate to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal degeneration, and to each other?Curr Opin Neurol. 2012 Dec;25(6):701-7. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e32835a269b. Curr Opin Neurol. 2012. PMID: 23041957 Review.
-
[Clinical and pathological spectrum of TDP-43 associated ALS].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2010 Nov;50(11):940-2. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.50.940. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2010. PMID: 21921519 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms of TDP-43 Misfolding and Pathology in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Feb 14;12:25. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00025. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30837838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To Be or Not To Be…Toxic-Is RNA Association With TDP-43 Complexes Deleterious or Protective in Neurodegeneration?Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Jan 10;6:154. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00154. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 31998750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pathobiology of TDP-43 C-Terminal Fragments in ALS and FTLD.Front Neurosci. 2019 Apr 11;13:335. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00335. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31031584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caspase-4 mediates cytoplasmic accumulation of TDP-43 in the primate brains.Acta Neuropathol. 2019 Jun;137(6):919-937. doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-01979-0. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Acta Neuropathol. 2019. PMID: 30810811 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase cleavage of iASPP potentiates its ability to inhibit p53 and NF-κB.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 15;6(40):42478-90. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6478. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26646590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buratti E, Baralle FE. Multiple roles of TDP-43 in gene expression, splicing regulation, and human disease. Front Biosci. 2008;13:867–878. - PubMed
-
- Buratti E, Baralle FE. Characterization and functional implications of the RNA binding properties of nuclear factor TDP-43, a novel splicing regulator of CFTR exon 9. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:36337–36343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

