The oncogenic lung cancer fusion kinase CD74-ROS activates a novel invasiveness pathway through E-Syt1 phosphorylation
- PMID: 22659450
- PMCID: PMC3753671
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3990
The oncogenic lung cancer fusion kinase CD74-ROS activates a novel invasiveness pathway through E-Syt1 phosphorylation
Abstract
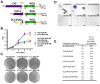
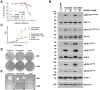
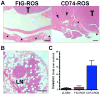
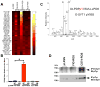
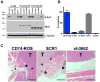
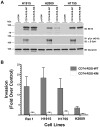
Patients with lung cancer often present with metastatic disease and therefore have a very poor prognosis. The recent discovery of several novel ROS receptor tyrosine kinase molecular alterations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) presents a therapeutic opportunity for the development of new targeted treatment strategies. Here, we report that the NSCLC-derived fusion CD74-ROS, which accounts for 30% of all ROS fusion kinases in NSCLC, is an active and oncogenic tyrosine kinase. We found that CD74-ROS-expressing cells were highly invasive in vitro and metastatic in vivo. Pharmacologic inhibition of CD74-ROS kinase activity reversed its transforming capacity by attenuating downstream signaling networks. Using quantitative phosphoproteomics, we uncovered a mechanism by which CD74-ROS activates a novel pathway driving cell invasion. Expression of CD74-ROS resulted in the phosphorylation of the extended synaptotagmin-like protein E-Syt1. Elimination of E-Syt1 expression drastically reduced invasiveness both in vitro and in vivo without modifying the oncogenic activity of CD74-ROS. Furthermore, expression of CD74-ROS in noninvasive NSCLC cell lines readily conferred invasive properties that paralleled the acquisition of E-Syt1 phosphorylation. Taken together, our findings indicate that E-Syt1 is a mediator of cancer cell invasion and molecularly define ROS fusion kinases as therapeutic targets in the treatment of NSCLC.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD74-ROS1 G2032R mutation transcriptionally up-regulates Twist1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells leading to increased migration, invasion, and resistance to crizotinib.Cancer Lett. 2018 May 28;422:19-28. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.02.032. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 29477381
-
CD74-ROS1 fusion transcripts in resected non-small cell lung carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2013 Oct;30(4):1675-80. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2630. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23877438
-
Efficacy of Crizotinib among Different Types of ROS1 Fusion Partners in Patients with ROS1-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2018 Jul;13(7):987-995. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.04.016. Epub 2018 Apr 25. J Thorac Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29704675
-
[A new target in non-small cell lung cancer: ROS1 fusion gene].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2013 Jan;35(1):1-4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2013.01.001. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23648291 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
-
ROS1 protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of ROS1 fusion protein-driven non-small cell lung cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Jul;121:202-212. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.04.022. Epub 2017 Apr 30. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28465216 Review.
Cited by
-
PF-06463922 is a potent and selective next-generation ROS1/ALK inhibitor capable of blocking crizotinib-resistant ROS1 mutations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Mar 17;112(11):3493-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1420785112. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25733882 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of β-sitosterol target proteins.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Nov 1;25(21):4976-4979. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.03.007. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 25804720 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing kinase intergenic-breakpoint rearrangements in a large-scale lung cancer population and real-world clinical outcomes.ESMO Open. 2022 Apr;7(2):100405. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100405. Epub 2022 Mar 16. ESMO Open. 2022. PMID: 35305401 Free PMC article.
-
Current treatment and novel insights regarding ROS1-targeted therapy in malignant tumors.Cancer Med. 2024 Apr;13(8):e7201. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7201. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38629293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synaptotagmin-7 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation via Chk1-p53 signaling.Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Aug 29;10:4283-4293. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S143619. eCollection 2017. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 28919777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acquaviva J, Wong R, Charest A. The multifaceted roles of the receptor tyrosine kinase ROS in development and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1795:37–52. - PubMed
-
- Charest A, Lane K, McMahon K, Park J, Preisinger E, Conroy H, et al. Fusion of FIG to the receptor tyrosine kinase ROS in a glioblastoma with an interstitial del(6)(q21q21) Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2003;37:58–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

