Hippocampal angiogenesis and progenitor cell proliferation are increased with antidepressant use in major depression
- PMID: 22652019
- PMCID: PMC3438317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.04.024
Hippocampal angiogenesis and progenitor cell proliferation are increased with antidepressant use in major depression
Abstract
Background: Adult neurogenesis is coupled to angiogenesis in neurogenic niches in the dentate gyrus (DG) and increased by antidepressants in rodents. We hypothesized that, in major depressive disorder (MDD), antidepressants increase neural progenitor cells (NPCs) and capillaries in the human DG.
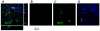
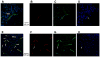
Methods: Neural progenitor cells and capillaries, detected on hippocampal sections by immunohistochemistry for neural stem cell protein, were quantified by stereology in matched MDDs (untreated, n = 12), MDD treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (MDD*SSRI, n = 6) or tricyclic antidepressants (MDD*TCA, n = 6), and nonpsychiatric control subjects (n = 12), all confirmed by psychological autopsy.
Results: The MDD*SSRI had a larger capillary area and more NPCs versus MDDs (p = .034 and p = .008, respectively) and control subjects (p = .010 and p = .002, respectively) in the whole DG, more NPCs in the anterior (pes, p = .042) and central (midbody, p = .004) DG, and greater capillary area in the pes (p = .002) and midbody (p = .021). The NPC number and capillary area correlated positively in the whole sample (R2 = .454, p < .001) and in treated subjects (R2 = .749, p = .001). We found no NPCs or antidepressant-related angiogenesis in CA1 and parahippocampal gyrus. The DG volume correlated positively with NPC number (p = .004) and capillary area (p < .001) and differed between groups in whole hippocampus (p = .013) and midbody (p = .036). Age negatively correlated with NPC number (p = .042), capillary area (p = .037), and bifurcations (p = .030). No gender effect was detected.
Conclusions: Antidepressants increase human hippocampal NPCs and angiogenesis selectively in the anterior and mid DG. These results raise the possibility of a causal relationship between angiogenesis and neurogenesis, as seen in other proliferating tissues, and support their possible role in the mechanism of action of antidepressants.
Copyright © 2012 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antidepressants increase neural progenitor cells in the human hippocampus.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 Oct;34(11):2376-89. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.75. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19606083 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal granule neuron number and dentate gyrus volume in antidepressant-treated and untreated major depression.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 May;38(6):1068-77. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.5. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23303074 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience Is Associated With Larger Dentate Gyrus, While Suicide Decedents With Major Depressive Disorder Have Fewer Granule Neurons.Biol Psychiatry. 2019 May 15;85(10):850-862. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.12.022. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30819514 Free PMC article.
-
Dentate gyrus neurogenesis and depression.Prog Brain Res. 2007;163:697-722. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(07)63038-6. Prog Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17765746 Review.
-
The role of neurotrophic factors in adult hippocampal neurogenesis, antidepressant treatments and animal models of depressive-like behavior.Behav Pharmacol. 2007 Sep;18(5-6):391-418. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e3282ee2aa8. Behav Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17762509 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular stress and epigenetic regulation in adult stem cells.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Sep 30;7(12):e202302083. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302083. Print 2024 Dec. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39348938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmeterol, a β2 Adrenergic Agonist, Promotes Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Region-Specific Manner.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 12;10:1000. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01000. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31572182 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiological mechanisms underlying sex-related differences in stress-related disorders: Effects of neuroactive steroids on the hippocampus.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2019 Oct;55:100796. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2019.100796. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31580837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modes of division and differentiation of neural stem cells.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Nov 18;374:112118. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112118. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31369774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Consequences of cancer treatments on adult hippocampal neurogenesis: implications for cognitive function and depressive symptoms.Neuro Oncol. 2014 Apr;16(4):476-92. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not321. Epub 2014 Jan 26. Neuro Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24470543 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aberg MA, Aberg ND, Palmer TD, Alborn AM, Carlsson-Skwirut C, Bang P, et al. IGF-I has a direct proliferative effect in adult hippocampal progenitor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003;24:23–40. - PubMed
-
- Asada M, Ebihara S, Yamanda S, Niu K, Okazaki T, Sora I, et al. Depletion of serotonin and selective inhibition of 2B receptor suppressed tumor angiogenesis by inhibiting endothelial nitric oxide synthase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation. Neoplasia. 2009;11:408–417. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bremner JD, Narayan M, Anderson ER, Staib LH, Miller HL, Charney DS. Hippocampal volume reduction in major depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:115–118. - PubMed
-
- Brook GA, Perez-Bouza A, Noth J, Nacimiento W. Astrocytes re-express nestin in deafferented target territories of the adult rat hippocampus. Neuroreport. 1999;10:1007–1011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

