Application of RNA silencing to plant disease resistance
- PMID: 22650989
- PMCID: PMC3503840
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-907X-3-5
Application of RNA silencing to plant disease resistance
Abstract
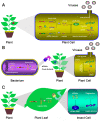
To reduce the losses caused by plant pathogens, plant biologists have adopted numerous methods to engineer resistant plants. Among them, RNA silencing-based resistance has been a powerful tool that has been used to engineer resistant crops during the last two decades. Based on this mechanism, diverse approaches were developed. In this review, we focus on the application of RNA silencing to produce plants that are resistant to plant viruses such as RNA and DNA viruses, viroids, insects, and the recent expansion to fungal pathogens.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Viroids and RNA silencing: mechanism, role in viroid pathogenicity and development of viroid-resistant plants.GM Crops. 2010 Mar-Apr;1(2):80-6. doi: 10.4161/gmcr.1.2.11871. GM Crops. 2010. PMID: 21865875 Review.
-
Catch Me If You Can! RNA Silencing-Based Improvement of Antiviral Plant Immunity.Viruses. 2019 Jul 23;11(7):673. doi: 10.3390/v11070673. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31340474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Back to the future.J Invertebr Pathol. 2015 Nov;132:1-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2015.07.009. Epub 2015 Jul 27. J Invertebr Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26225455 Review.
-
Antiviral strategies in plants based on RNA silencing.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov-Dec;1809(11-12):722-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.05.011. Epub 2011 May 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21652000 Review.
-
An internet-based bioinformatics toolkit for plant biosecurity diagnosis and surveillance of viruses and viroids.BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Jan 11;18(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1428-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28077064 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Host-induced gene silencing compromises Verticillium wilt in tomato and Arabidopsis.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 Jan;19(1):77-89. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12500. Epub 2016 Dec 4. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 27749994 Free PMC article.
-
A virus-derived short hairpin RNA confers resistance against sugarcane mosaic virus in transgenic sugarcane.Transgenic Res. 2018 Apr;27(2):203-210. doi: 10.1007/s11248-018-0066-1. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Transgenic Res. 2018. PMID: 29492792
-
Down-regulation of Fusarium oxysporum endogenous genes by Host-Delivered RNA interference enhances disease resistance.Front Chem. 2015 Jan 20;3:1. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2015.00001. eCollection 2015. Front Chem. 2015. PMID: 25654075 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas-Mediated Resistance against Viruses in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 19;23(4):2303. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042303. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Foliar Delivery of siRNA Particles for Treating Viral Infections in Agricultural Grapevines.Adv Funct Mater. 2021 Jul 10;31(44):2101003. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202101003. eCollection 2021 Oct 26. Adv Funct Mater. 2021. PMID: 34744552 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
