FGF23 acts directly on renal proximal tubules to induce phosphaturia through activation of the ERK1/2-SGK1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 22647968
- PMCID: PMC3419258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2012.05.015
FGF23 acts directly on renal proximal tubules to induce phosphaturia through activation of the ERK1/2-SGK1 signaling pathway
Abstract
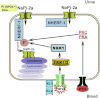
Fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) is a bone-derived endocrine regulator of phosphate homeostasis which inhibits renal tubular phosphate reabsorption. Binding of circulating FGF23 to FGF receptors in the cell membrane requires the concurrent presence of the co-receptor αKlotho. It is still controversial whether αKlotho is expressed in the kidney proximal tubule, the principal site of phosphate reabsorption. Hence, it has remained an enigma as to how FGF23 downregulates renal phosphate reabsorption. Here, we show that renal proximal tubular cells do express the co-receptor αKlotho together with cognate FGF receptors, and that FGF23 directly downregulates membrane expression of the sodium-phosphate cotransporter NaPi-2a by serine phosphorylation of the scaffolding protein Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor (NHERF)-1 through ERK1/2 and serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase-1 signaling.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
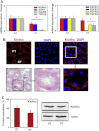
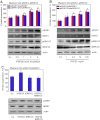
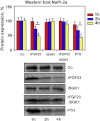

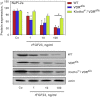
Similar articles
-
FGF23-Klotho signaling axis in the kidney.Bone. 2017 Jul;100:62-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Bone. 2017. PMID: 27622885 Review.
-
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D Maintains Brush Border Membrane NaPi2a and Attenuates Phosphaturia in Hyp Mice.Endocrinology. 2019 Oct 1;160(10):2204-2214. doi: 10.1210/en.2019-00186. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 31237611 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo evidence for an interplay of FGF23/Klotho/PTH axis on the phosphate handling in renal proximal tubules.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):F1261-F1270. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00650.2017. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29993278 Free PMC article.
-
FGF23 regulates renal sodium handling and blood pressure.EMBO Mol Med. 2014 Jun;6(6):744-59. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201303716. Epub 2014 Apr 6. EMBO Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24797667 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic Actions of FGF23.Toxicol Pathol. 2017 Oct;45(7):904-910. doi: 10.1177/0192623317737469. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Toxicol Pathol. 2017. PMID: 29096595 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond mineral metabolism, is there an interplay between FGF23 and vitamin D in innate immunity?Pediatr Nephrol. 2013 Apr;28(4):577-82. doi: 10.1007/s00467-012-2336-0. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23117582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aldosterone Is Positively Associated With Circulating FGF23 Levels in Chronic Kidney Disease Across Four Species, and May Drive FGF23 Secretion Directly.Front Physiol. 2021 Apr 29;12:649921. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.649921. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33995120 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D Supplementation for 12 Months in Older Adults Alters Regulators of Bone Metabolism but Does Not Change Wnt Signaling Pathway Markers.JBMR Plus. 2022 Mar 24;6(5):e10619. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10619. eCollection 2022 May. JBMR Plus. 2022. PMID: 35509637 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Teriparatide in Hyperphosphatemic Familial Tumor Calcinosis: Evaluating the Interaction Between FGF23 and PTH on the Phosphaturic Effect.Calcif Tissue Int. 2022 Jul;111(1):102-106. doi: 10.1007/s00223-022-00969-x. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022. PMID: 35338393
-
Renal FGF23 signaling depends on redox protein Memo1 and promotes orthovanadate-sensitive protein phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activity.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep;17(3):705-722. doi: 10.1007/s12079-022-00710-1. Epub 2022 Nov 25. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36434320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The ADHR Consortium Autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets is associated with mutations in FGF23. Nat Genet. 2000;26:345–348. - PubMed
-
- Urakawa I., Yamazaki Y., Shimada T., Iijima K., Hasegawa H., Okawa K. Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for FGF23. Nature. 2006;444:770–774. - PubMed
-
- Kuro-o M., Matsumura Y., Aizawa H., Kawaguchi H., Suga T., Utsugi T. Mutation of the mouse Klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature. 1997;390:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Baum M., Schiavi S., Dwarakanath V., Quigley R. Effect of fibroblast growth factor-23 on phosphate transport in proximal tubules. Kidney Int. 2005;68:1148–1153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

