Rapid determination of multiple linear kinase substrate motifs by mass spectrometry
- PMID: 22633412
- PMCID: PMC3366114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.04.011
Rapid determination of multiple linear kinase substrate motifs by mass spectrometry
Abstract
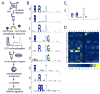
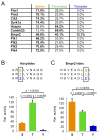
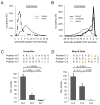
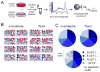
Kinase-substrate recognition depends on the chemical properties of the phosphorylatable residue as well as the surrounding linear sequence motif. Detailed knowledge of these characteristics increases the confidence of linking identified phosphorylation sites to kinases, predicting phosphorylation sites, and designing optimal peptide substrates. Here, we present a mass spectrometry-based approach for determining linear kinase substrate motifs by elaborating the positional and chemical preference of the kinase for a phosphorylatable residue using libraries of naturally-occurring peptides that are amenable to peptide identification by commonly used proteomics platforms. We applied this approach to a structurally and functionally diverse set of purified kinases, which recapitulated their previously described substrate motifs and discovered additional ones, including preferences of certain kinases for phosphorylatable residues adjacent to peptide termini. Furthermore, we identify specific and distinguishable motif elements for the four members of the polo-like kinase (Plk) family and verify members of these motif elements for Plk1 in vivo.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of a consensus motif for Plk (Polo-like kinase) phosphorylation reveals Myt1 as a Plk1 substrate.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jul 11;278(28):25277-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C300126200. Epub 2003 May 8. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12738781
-
Polo-box domain: a versatile mediator of polo-like kinase function.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Jun;67(12):1957-70. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0279-9. Epub 2010 Feb 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20148280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide and protein library screening defines optimal substrate motifs for AKT/PKB.J Biol Chem. 2000 Nov 17;275(46):36108-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005497200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10945990
-
Identification of potential Plk1 targets in a cell-cycle specific proteome through structural dynamics of kinase and Polo box-mediated interactions.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 15;8(8):e70843. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070843. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967120 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and enzoinformatics perspectives of targeting Polo-like kinase 1 in cancer therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2019 Jun;56:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.004. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019. PMID: 29122685 Review.
Cited by
-
Structures of Down syndrome kinases, DYRKs, reveal mechanisms of kinase activation and substrate recognition.Structure. 2013 Jun 4;21(6):986-96. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.03.012. Epub 2013 May 9. Structure. 2013. PMID: 23665168 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale Discovery of Substrates of the Human Kinome.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 19;9(1):10503. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46385-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31324866 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Identification of Protein Kinase Phosphorylation Site Motifs Using Combinatorial Peptide Libraries.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1360:203-16. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3073-9_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26501912 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry-Based Discovery of in vitro Kinome Substrates.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2020;9(1):A0082. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0082. Epub 2020 Mar 28. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2020. PMID: 32547896 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing Protein Kinase Substrate Specificity Using the Proteomic Peptide Library (ProPeL) Approach.Curr Protoc Chem Biol. 2018 Jun;10(2):e38. doi: 10.1002/cpch.38. Curr Protoc Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29927115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander J, Lim D, Joughin BA, Hegemann B, Hutchins JR, Ehrenberger T, Ivins F, Sessa F, Hudecz O, Nigg EA, et al. Spatial exclusivity combined with positive and negative selection of phosphorylation motifs is the basis for context-dependent mitotic signaling. Sci Signal. 2011;4:ra42. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barr FA, Sillje HH, Nigg EA. Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2004;5:429–440. - PubMed
-
- Bullock AN, Debreczeni J, Amos AL, Knapp S, Turk BE. Structure and substrate specificity of the Pim-1 kinase. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:41675–41682. - PubMed
-
- Campbell LE, Proud CG. Differing substrate specificities of members of the DYRK family of arginine-directed protein kinases. FEBS Lett. 2002;510:31–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

