Human papillomavirus type 8 E6 oncoprotein inhibits transcription of the PDZ protein syntenin-2
- PMID: 22623796
- PMCID: PMC3421679
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00132-12
Human papillomavirus type 8 E6 oncoprotein inhibits transcription of the PDZ protein syntenin-2
Abstract
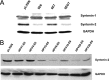
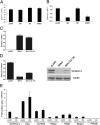
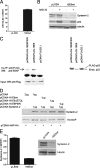
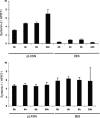
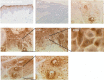
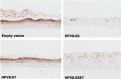
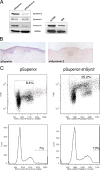
The E6 proteins from high-risk alpha human papillomavirus (HPV) types (e.g., HPV16) are characterized by the presence of a PDZ-binding motif through which they interact with a number of cellular PDZ domain-containing substrates and cooperate in their degradation. The ability of these E6 proteins to bind to PDZ domain proteins correlates with the oncogenic potential of the virus. The E6 proteins of oncogenic HPV from the genus Betapapillomavirus (betaPV, e.g., HPV8) do not encode a PDZ-binding motif. We found that the PDZ domain protein syntenin-2 is transcriptionally downregulated in primary human epidermal keratinocytes (PHEK) by HPV8 E6. The mRNA levels of the known HPV16 E6 PDZ protein targets Dlg, Scribble, Magi-1, Magi-3, PSD95, and Mupp1 were not changed by HPV8 E6. Decreased protein levels of syntenin-2 were observed in cell extracts from PHEK expressing HPV5, -8, -16, -20, and -38 E6 but not in HPV1 and -4 E6-positive keratinocytes. Surprisingly, HPV16 E6 also repressed transcription of syntenin-2 but with a much lower efficiency than HPV8 E6. In healthy human skin, syntenin-2 expression is localized in suprabasal epidermal layers. In organotypic skin cultures, the differentiation-dependent expression of syntenin-2 was absent in HPV8 E6- and E6E7-expressing cells. In basal cell carcinomas of the skin, syntenin-2 was not detectable, whereas in squamous cell carcinomas, expression was located in differentiated areas. Short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of syntenin-2 led to an inhibition of differentiation and an increase in the proliferation capacity in PHEK. These results identified syntenin-2 as the first PDZ domain protein controlled by HPV8 and HPV16 at the mRNA level.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beta-Genus Human Papillomavirus 8 E6 Destabilizes the Host Genome by Promoting p300 Degradation.Viruses. 2021 Aug 21;13(8):1662. doi: 10.3390/v13081662. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HPV8-E6 Interferes with Syntenin-2 Expression through Deregulation of Differentiation, Methylation and Phosphatidylinositide-Kinase Dependent Mechanisms.Front Microbiol. 2017 Sep 8;8:1724. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01724. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28970821 Free PMC article.
-
The E6 oncoprotein from HPV16 enhances the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway in skin epidermis in vivo.Mol Cancer Res. 2012 Feb;10(2):250-8. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0287. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Mol Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22160870 Free PMC article.
-
High-Risk Mucosal Human Papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) E6 Protein and Cutaneous HPV5 and HPV8 E6 Proteins Employ Distinct Strategies To Interfere with Interferon Regulatory Factor 3-Mediated Beta Interferon Expression.J Virol. 2022 May 25;96(10):e0187521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01875-21. Epub 2022 Apr 27. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35475668 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifunctional Protein Syntenin-1: Regulator of Exosome Biogenesis, Cellular Function, and Tumor Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 29;24(11):9418. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119418. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298370 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analysis of Alpha and Beta HPV E6 Oncoproteins: Insights into Functional Distinctions and Divergent Mechanisms of Pathogenesis.Viruses. 2023 Nov 14;15(11):2253. doi: 10.3390/v15112253. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38005929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beta-Genus Human Papillomavirus 8 E6 Destabilizes the Host Genome by Promoting p300 Degradation.Viruses. 2021 Aug 21;13(8):1662. doi: 10.3390/v13081662. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay of UV and cutaneous papillomavirus infection in skin cancer development.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Nov 30;13(11):e1006723. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006723. eCollection 2017 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 29190285 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of MDA-9/Syntenin (SDCBP) expression in the microenvironment dampens tumor-supporting inflammation and inhibits melanoma metastasis.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):46848-46861. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10040. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27341128 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic approaches to the study of papillomavirus-host interactions.Virology. 2013 Jan 5;435(1):57-69. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.09.046. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23217616 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akgül B, et al. 2011. Upregulation of lipocalin-2 in human papillomavirus-positive keratinocytes and cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas. J. Gen. Virol. 92:395–401 - PubMed
-
- Akgül B, et al. 2010. Human papillomavirus 5 and 8 E6 downregulate interleukin-8 secretion in primary human keratinocytes. J. Gen. Virol. 91:888–892 - PubMed
-
- Akgül B, Cooke JC, Storey A. 2006. HPV-associated skin disease. J. Pathol. 208:165–175 - PubMed
-
- Akgül B, et al. 2005. The E7 protein of cutaneous human papillomavirus type 8 causes invasion of human keratinocytes into the dermis in organotypic cultures of skin. Cancer Res. 65:2216–2223 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

