The Fanconi anaemia components UBE2T and FANCM are functionally linked to nucleotide excision repair
- PMID: 22615860
- PMCID: PMC3352854
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036970
The Fanconi anaemia components UBE2T and FANCM are functionally linked to nucleotide excision repair
Abstract
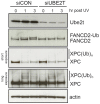
The many proteins that function in the Fanconi anaemia (FA) monoubiquitylation pathway initiate replicative DNA crosslink repair. However, it is not clear whether individual FA genes participate in DNA repair pathways other than homologous recombination and translesion bypass. Here we show that avian DT40 cell knockouts of two integral FA genes--UBE2T and FANCM are unexpectedly sensitive to UV-induced DNA damage. Comprehensive genetic dissection experiments indicate that both of these FA genes collaborate to promote nucleotide excision repair rather than translesion bypass to protect cells form UV genotoxicity. Furthermore, UBE2T deficiency impacts on the efficient removal of the UV-induced photolesion cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer. Therefore, this work reveals that the FA pathway shares two components with nucleotide excision repair, intimating not only crosstalk between the two major repair pathways, but also potentially identifying a UBE2T-mediated ubiquitin-signalling response pathway that contributes to nucleotide excision repair.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
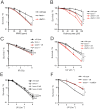
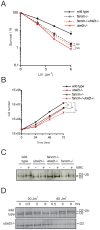
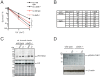
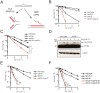
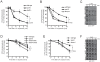
Similar articles
-
AluY-mediated germline deletion, duplication and somatic stem cell reversion in UBE2T defines a new subtype of Fanconi anemia.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Sep 15;24(18):5093-108. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv227. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 26085575 Free PMC article.
-
FANCM and FAAP24 function in ATR-mediated checkpoint signaling independently of the Fanconi anemia core complex.Mol Cell. 2008 Nov 7;32(3):313-24. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.10.014. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18995830
-
Recent discoveries in the molecular pathogenesis of the inherited bone marrow failure syndrome Fanconi anemia.Blood Rev. 2017 May;31(3):93-99. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Blood Rev. 2017. PMID: 27760710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between the nucleotide excision repair and Fanconi anemia/BRCA pathways.DNA Repair (Amst). 2014 Jul;19:130-4. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.03.019. Epub 2014 Apr 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014. PMID: 24768451
-
The Fanconi anemia pathway: insights from somatic cell genetics using DT40 cell line.Mutat Res. 2009 Jul 31;668(1-2):92-102. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.12.012. Epub 2009 Jan 17. Mutat Res. 2009. PMID: 19622405 Review.
Cited by
-
FANCJ localization by mismatch repair is vital to maintain genomic integrity after UV irradiation.Cancer Res. 2014 Feb 1;74(3):932-44. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2474. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24351291 Free PMC article.
-
Structure analysis of FAAP24 reveals single-stranded DNA-binding activity and domain functions in DNA damage response.Cell Res. 2013 Oct;23(10):1215-28. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.124. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23999858 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T in colorectal cancers and clinical implications.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):275. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12138. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 33014154 Free PMC article.
-
UBE2T Contributes to the Prognosis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Pathol Oncol Res. 2021 Apr 9;27:632531. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.632531. eCollection 2021. Pathol Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34257599 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and disease association of E2-conjugating enzymes: lessons from UBE2T and UBE2L3.Biochem J. 2016 Oct 15;473(20):3401-3419. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160028. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27729585 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garcia-Higuera I, Taniguchi T, Ganesan S, Meyn MS, Timmers C, et al. Interaction of the Fanconi anemia proteins and BRCA1 in a common pathway. Mol Cell. 2001;7:249–262. - PubMed
-
- Liu T, Ghosal G, Yuan J, Chen J, Huang J. FAN1 acts with FANCI-FANCD2 to promote DNA interstrand cross-link repair. Science. 2010;329:693–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

