Increased plasma levels of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (sFlt-1) in women by moderate exercise and increased plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in overweight/obese women
- PMID: 22609636
- PMCID: PMC3449013
- DOI: 10.1097/CEJ.0b013e328353ed81
Increased plasma levels of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (sFlt-1) in women by moderate exercise and increased plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in overweight/obese women
Abstract
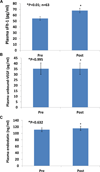
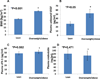
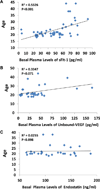
The incidence of breast cancer is increasing worldwide, and this seems to be related to an increase in lifestyle risk factors, including physical inactivity and overweight/obesity. We have reported previously that exercise induced a circulating angiostatic phenotype characterized by increased soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1) and endostatin and decreased unbound vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in men. However, there are no data on women. The present study determines the following: (a) whether moderate exercise increased sFlt-1 and endostatin and decreased unbound VEGF in the circulation of adult female volunteers and (b) whether overweight/obese women have a higher plasma level of unbound VEGF than lean women. A total of 72 African American and White adult women volunteers ranging in age from 18 to 44 years were enrolled in the exercise study. All the participants walked on a treadmill for 30 min at a moderate intensity (55-59% heart rate reserve), and oxygen consumption (VO(2)) was quantified utilizing a metabolic cart. We obtained blood samples before and immediately after exercise from 63 participants. ELISA assays showed that the plasma levels of sFlt-1 were 67.8±3.7 pg/ml immediately after exercise (30 min), significantly higher than the basal levels, 54.5±3.3 pg/ml, before exercise (P<0.01; n=63). There was no significant difference in the % increase in the sFlt-1 levels after exercise between African American and White (P=0.533) women or between lean and overweight/obese women (P=0.892). There was no significant difference in the plasma levels of unbound VEGF (35.28±5.47 vs. 35.23±4.96 pg/ml; P=0.99) or endostatin (111.12±5.48 vs. 115.45±7.15 ng/ml; P=0.63) before and after exercise. The basal plasma levels of unbound VEGF in overweight/obese women were 52.26±9.6 pg/ml, significantly higher than the basal levels of unbound VEGF in lean women, 27.34±4.99 pg/ml (P<0.05). The results support our hypothesis that exercise-induced plasma levels of sFlt-1 could be an important clinical biomarker to explore the mechanisms of exercise training in reducing the progression of breast cancer and that VEGF is an important biomarker in obesity and obesity-related cancer progression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exercise increases soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (sFlt-1) in circulation of healthy volunteers.Med Sci Monit. 2006 Feb;12(2):CR45-50. Epub 2006 Jan 26. Med Sci Monit. 2006. PMID: 16449946
-
Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Soluble fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase-1 as Biomarkers for Endometrial Remodeling Across the Menstrual Cycle.Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Jan 1;137(1):82-90. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004171. Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33278289 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated soluble VEGF receptor sFlt-1 correlates with endothelial injury in IgA nephropathy.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 9;9(7):e101779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101779. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25007257 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of free and complexed soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, Flt-1, in fluid samples: development and application of two new immunoassays.Clin Sci (Lond). 2001 May;100(5):567-75. Clin Sci (Lond). 2001. PMID: 11294698
-
The relationship between circulating tissue transglutaminase, soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1, soluble endoglin and vascular endothelial growth factor in pre-eclampsia.J Hum Hypertens. 2016 Dec;30(12):788-793. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2016.32. Epub 2016 May 12. J Hum Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27169826
Cited by
-
The effects of Spirulina Platensis on anthropometric indices, appetite, lipid profile and serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in obese individuals: a randomized double blinded placebo controlled trial.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Apr 21;17(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1670-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28431534 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of physical activity on preeclampsia and angiogenic markers in the Finnish Genetics of Pre-eclampsia Consortium (FINNPEC) cohort.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2325480. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2325480. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 38466911 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise increases serum endostatin levels in female and male patients with diabetes and controls.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014 Jan 6;13:6. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-13-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014. PMID: 24393402 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bevacuzimab May Be Less Effective in Obese Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019 Jun;50(2):214-220. doi: 10.1007/s12029-017-0047-2. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019. PMID: 29302856
-
Obese melanocortin-4 receptor-deficient rats exhibit augmented angiogenic balance and vasorelaxation during pregnancy.Physiol Rep. 2013 Sep 1;1(4):e00081. doi: 10.1002/phy2.81. Physiol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24159378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey AP, Shparago M, Gu JW. Exercise Increases Soluble Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 (sFlt-1) in Circulation of Healthy Volunteers. Medical Science Monitor. 2006;12:CR45–CR50. - PubMed
-
- Bardia A, Hartmann LC, Vachon CM, Vierkant RA, Wang AH, Olson JE, et al. Recreational physical activity and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer based on hormone receptor status. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:2478–2483. - PubMed
-
- Cai J, Jiang WG, Grant MS, Boulton M. Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits angiogenesis via regulated intracellular proteolysis of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:3604–3613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

