Differential modulation of drug-induced structural and functional plasticity of dendritic spines
- PMID: 22596350
- PMCID: PMC3400837
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.112.078162
Differential modulation of drug-induced structural and functional plasticity of dendritic spines
Abstract
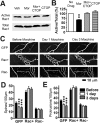
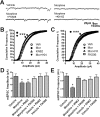
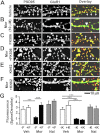
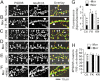
Drug-induced plasticity of excitatory synapses has been proposed to be the cellular mechanism underlying the aberrant learning associated with addiction. Exposure to various drugs of abuse causes both morphological plasticity of dendritic spines and functional plasticity of excitatory synaptic transmission. Chronic activation of μ-opioid receptors (MOR) in cultured hippocampal neurons causes two forms of synaptic plasticity: loss of dendritic spines and loss of synaptic α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors. With use of live imaging, patch-clamp electrophysiology, and immunocytochemistry, the present study reveals that these two forms of synaptic plasticity are mediated by separate, but interactive, intracellular signaling cascades. The inhibition of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II with 1-[N,O-bis(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-N-methyl-l-tyrosyl]-4-phenylpiperazine (KN-62) blocks MOR-mediated structural plasticity of dendritic spines, but not MOR-mediated cellular redistribution of GluR1 and GluR2 AMPA receptor subunits. In contrast, the inhibition of calcineurin with tacrolimus (FK506) blocks both cellular processes. These findings support the idea that drug-induced structural and functional plasticity of dendritic spines is mediated by divergent, but interactive, signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prolonged ampakine exposure prunes dendritic spines and increases presynaptic release probability for enhanced long-term potentiation in the hippocampus.Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Sep;40(5):2766-76. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12638. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Eur J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24925283
-
Bidirectional effects of fentanyl on dendritic spines and AMPA receptors depend upon the internalization of mu opioid receptors.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 Aug;34(9):2097-111. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.34. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19295508 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptopodin regulates plasticity of dendritic spines in hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2009 Jan 28;29(4):1017-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5528-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19176811 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of morphine on brain plasticity.Neurologia. 2015 Apr;30(3):176-80. doi: 10.1016/j.nrl.2014.08.004. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Neurologia. 2015. PMID: 25444409 Review. English, Spanish.
-
Excitatory amino acid involvement in dendritic spine formation, maintenance and remodelling.J Physiol. 2010 Jan 1;588(Pt 1):107-16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.178905. Epub 2009 Nov 23. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19933758 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tau phosphorylation and tau mislocalization mediate soluble Aβ oligomer-induced AMPA glutamate receptor signaling deficits.Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Apr;39(7):1214-24. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12507. Eur J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24713000 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of neuronal dysfunction in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 May;78(9):4283-4303. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03785-y. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33585975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of neuroimmune signaling and glutamate plasticity in addiction.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Feb 21;18(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02072-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 33612110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pin1 mediates Aβ42-induced dendritic spine loss.Sci Signal. 2018 Mar 20;11(522):eaap8734. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aap8734. Sci Signal. 2018. PMID: 29559586 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Chronic Morphine Consumption on Synaptic Plasticity of Rat's Hippocampus: A Transmission Electron Microscopy Study.Neurol Res Int. 2013;2013:290414. doi: 10.1155/2013/290414. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Neurol Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24379975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Billa SK, Liu J, Bjorklund NL, Sinha N, Fu Y, Shinnick-Gallagher P, Morón JA. (2010a) Increased insertion of glutamate receptor 2-lacking α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors at hippocampal synapses upon repeated morphine administration. Mol Pharmacol 77:874–883 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K02 DA025048/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA016674/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA000564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P32-GM00847/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA020582/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007234/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA000564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA020582/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008471/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA000564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA007339/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32-DA07234/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50-DA011806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA016674/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32GM008471/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA011806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA007339/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
