Poxviral protein A46 antagonizes Toll-like receptor 4 signaling by targeting BB loop motifs in Toll-IL-1 receptor adaptor proteins to disrupt receptor:adaptor interactions
- PMID: 22593572
- PMCID: PMC3391086
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.349225
Poxviral protein A46 antagonizes Toll-like receptor 4 signaling by targeting BB loop motifs in Toll-IL-1 receptor adaptor proteins to disrupt receptor:adaptor interactions
Abstract
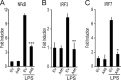
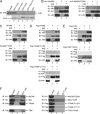
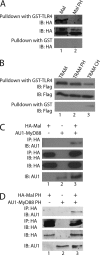
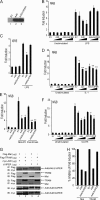
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) have an anti-viral role in that they detect viruses, leading to cytokine and IFN induction, and as such are targeted by viruses for immune evasion. TLR4, although best known for its role in recognizing bacterial LPS, is also strongly implicated in the immune response to viruses. We previously showed that the poxviral protein A46 inhibits TLR4 signaling and interacts with Toll-IL-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing proteins of the receptor complex. However the exact molecular mechanism whereby A46 disrupts TLR4 signaling remains to be established, and may yield insight into how the TLR4 complex functions, since viruses often optimally target key residues and motifs on host proteins for maximal efficiency. Here we show that A46 targets the BB loop motif of TIR proteins and thereby disrupts receptor:adaptor (TLR4:Mal and TLR4:TRAM), but not receptor:receptor (TLR4:TLR4) nor adaptor:adaptor (Mal:MyD88, TRAM:TRIF, and Mal:Mal) TIR interactions. The requirement for an intact BB loop for TIR adaptor interactions correlated with the protein:protein interfaces antagonized by A46. We previously discovered a peptide fragment derived from A46 termed VIPER (Viral Inhibitory Peptide of TLR4), which specifically inhibits TLR4 responses. Here we demonstrate that the region of A46 from which VIPER is derived represents the TLR4-specific inhibitory motif of the intact protein, and is essential for A46:TRAM interactions. This study provides the molecular basis for pathogen subversion of TLR4 signaling and clarifies the importance of TIR motif BB loops, which have been selected for viral antagonism, in the formation of the TLR4 complex.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Viral inhibitory peptide of TLR4, a peptide derived from vaccinia protein A46, specifically inhibits TLR4 by directly targeting MyD88 adaptor-like and TRIF-related adaptor molecule.J Immunol. 2010 Oct 1;185(7):4261-71. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002013. Epub 2010 Aug 27. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20802145
-
Poxvirus A46 protein binds to TIR domain-containing Mal/TIRAP via an α-helical sub-domain.Mol Immunol. 2011 Sep;48(15-16):2144-50. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2011.07.014. Epub 2011 Aug 9. Mol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21831443
-
Structure of vaccinia virus A46, an inhibitor of TLR4 signaling pathway, shows the conformation of VIPER motif.Protein Sci. 2014 Jul;23(7):906-14. doi: 10.1002/pro.2472. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Protein Sci. 2014. PMID: 24723367 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interfaces between TICAM-2/TRAM and TICAM-1/TRIF in TLR4 signaling.Biochem Soc Trans. 2017 Aug 15;45(4):929-935. doi: 10.1042/BST20160259. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017. PMID: 28630139 Review.
-
Microbial recognition by Toll-like receptors.J Dermatol Sci. 2004 Apr;34(2):73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2003.10.002. J Dermatol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15033189 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated approaches for the recognition of small molecule inhibitors for Toll-like receptor 4.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Jul 22;21:3680-3689. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.07.026. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37576745 Free PMC article.
-
Solution structure of the TLR adaptor MAL/TIRAP reveals an intact BB loop and supports MAL Cys91 glutathionylation for signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Aug 8;114(32):E6480-E6489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1701868114. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28739909 Free PMC article.
-
Leaky scanning translation generates a second A49 protein that contributes to vaccinia virus virulence.J Gen Virol. 2020 May;101(5):533-541. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001386. Epub 2020 Feb 24. J Gen Virol. 2020. PMID: 32100702 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB activation is a turn on for vaccinia virus phosphoprotein A49 to turn off NF-κB activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Mar 19;116(12):5699-5704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1813504116. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30819886 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of TLR4 signaling by TRAM-derived decoy peptides in vitro and in vivo.J Immunol. 2013 Mar 1;190(5):2263-72. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202703. Epub 2013 Jan 23. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23345333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keating S. E., Baran M., Bowie A. G. (2011) Cytosolic DNA sensors regulating type I interferon induction. Trends Immunol. 32, 574–581 - PubMed
-
- Akira S., Uematsu S., Takeuchi O. (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124, 783–801 - PubMed
-
- Kawai T., Akira S. (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 11, 373–384 - PubMed
-
- Kawai T., Akira S. (2008) Toll-like receptor and RIG-I-like receptor signaling. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1143, 1–20 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

