Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human keratinocytes
- PMID: 22592159
- PMCID: PMC3423535
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2012.78
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human keratinocytes
Abstract
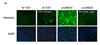
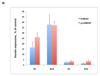
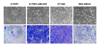
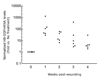
We have shown that autocrine proliferation of human keratinocytes (KCs) is strongly dependent upon amphiregulin (AREG), whereas blockade of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) inhibits KC migration in scratch wound assays. Here we demonstrate that expression of soluble HB-EGF (sHB-EGF) or full-length transmembrane HB-EGF (proHB-EGF), but not proAREG, results in profound increases in KC migration and invasiveness in monolayer culture. Coincident with these changes, HB-EGF significantly decreases mRNA expression of several epithelial markers including keratins 1, 5, 10, and 14 while increasing expression of markers of cellular motility including SNAI1, ZEB1, COX-2, and MMP1. Immunostaining revealed HB-EGF-induced expression of the mesenchymal protein vimentin and decreased expression of E-cadherin, as well as nuclear translocation of β-catenin. Suggestive of a trade-off between KC motility and proliferation, overexpression of HB-EGF also reduced KC growth by >90%. We also show that HB-EGF is strongly induced in regenerating epidermis after partial-thickness wounding of human skin. Taken together, our data suggest that expression of HB-EGF in human KCs triggers a migratory and invasive phenotype with many features of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which may be beneficial in the context of cutaneous wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures









Comment in
-
HB-EGF, the growth factor that accelerates keratinocyte migration, but slows proliferation.J Invest Dermatol. 2012 Sep;132(9):2129-30. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.225. J Invest Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 22895444
Similar articles
-
Metalloproteinase-mediated, context-dependent function of amphiregulin and HB-EGF in human keratinocytes and skin.J Invest Dermatol. 2010 Jan;130(1):295-304. doi: 10.1038/jid.2009.211. J Invest Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 19609315 Free PMC article.
-
HB-EGF, the growth factor that accelerates keratinocyte migration, but slows proliferation.J Invest Dermatol. 2012 Sep;132(9):2129-30. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.225. J Invest Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 22895444
-
Membrane-bound heparin-binding epidermal growth factor like growth factor regulates E-cadherin expression in pancreatic carcinoma cells.Cancer Res. 2007 Sep 15;67(18):8486-93. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0498. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17875687
-
Autocrine regulation of keratinocytes: the emerging role of heparin-binding, epidermal growth factor-related growth factors.J Invest Dermatol. 1998 Nov;111(5):715-21. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.1998.00390.x. J Invest Dermatol. 1998. PMID: 9804327 Review.
-
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor: a juxtacrine growth factor.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000 Dec;11(4):335-44. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(00)00013-7. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000. PMID: 10959080 Review.
Cited by
-
Recombinant Prolidase Activates EGFR-Dependent Cell Growth in an Experimental Model of Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Implication for Wound Healing.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Mar 30;9:876348. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.876348. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35433830 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant expression of the UPF1 RNA surveillance gene disturbs keratinocyte homeostasis by stabilizing AREG.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Apr;45(4):1163-1175. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4487. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32124941 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of serum from sepsis patients on epithelial cell migration in vitro: a case control study.J Transl Med. 2017 Jan 13;15(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-1110-7. J Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28086962 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tissue repair and fibrosis.Cell Tissue Res. 2016 Sep;365(3):495-506. doi: 10.1007/s00441-016-2464-0. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Cell Tissue Res. 2016. PMID: 27461257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local cortisol activation is involved in EGF-induced immunosuppression.Dermatoendocrinol. 2017 Dec 26;9(1):e1412018. doi: 10.1080/19381980.2017.1412018. eCollection 2017. Dermatoendocrinol. 2017. PMID: 29484105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cano A, Perez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, et al. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:76–83. - PubMed
-
- Coffey RJ, Jr, Derynck R, Wilcox JN, Bringman TS, Goustin AS, Moses HL, et al. Production and auto-induction of transforming growth factor-alpha in human keratinocytes. Nature. 1987;328:817–820. - PubMed
-
- Das SK, Wang XN, Paria BC, Damm D, Abraham JA, Klagsbrun M, et al. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor gene is induced in the mouse uterus temporally by the blastocyst solely at the site of its apposition: a possible ligand for interaction with blastocyst EGF- receptor in implantation. Development. 1994;120:1071–1083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

