ARFI elastography for the evaluation of diffuse thyroid gland pathology: Preliminary results
- PMID: 22590672
- PMCID: PMC3351686
- DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i4.174
ARFI elastography for the evaluation of diffuse thyroid gland pathology: Preliminary results
Abstract
Aim: To assess whether acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography can differentiate normal from pathological thyroid parenchyma.
Methods: We evaluated 136 subjects (mean age 45.8 ± 15.6 years, 106 women and 30 men): 44 (32.3%) without thyroid pathology, 48 (35.3%) with Basedow-Graves' disease (GD), 37 (27.2%) with chronic autoimmune thyroiditis (CAT; diagnosed by specific tests), 4 (2.9%) with diffuse thyroid goiter and 3 (2.2%) cases with thyroid pathology induced by amiodarone. In all patients, 10 elastographic measurements were made in the right thyroid lobe and 10 in the left thyroid lobe, using a 1-4.5 MHZ convex probe and a 4-9 MHz linear probe, respectively. Median values were calculated for thyroid stiffness and expressed in meters/second (m/s).
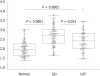
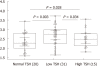
Results: Thyroid stiffness (TS) assessed by means of ARFI in healthy subjects (2 ± 0.40 m/s) was significantly lower than in GD (2.67 ± 0.53 m/s) (P < 0.0001) and CAT patients (2.43 ± 0.58 m/s) (P = 0.0002), but the differences were not significant between GD vs CAT patients (P = 0.053). The optimal cut-off value for the prediction of diffuse thyroid pathology was 2.36 m/s. For this cut-off value, TS had 62.5% sensitivity, 79.5% specificity, 87.6% predictive positive value, 55.5% negative predictive value and 72.7% accuracy for the presence of diffuse thyroid gland pathology (AUROC = 0.804). There were no significant differences between the TS values obtained with linear vs convex probes and when 5 vs 10 measurements were taken in each lobe (median values).
Conclusion: ARFI seems to be a useful method for the assessment of diffuse thyroid gland pathology.
Keywords: Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography; Thyroid pathology; Thyroid stiffness.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thyroid stiffness assessment by acoustic radiation force impulse elastography (ARFI).Ultraschall Med. 2011 Jun;32(3):281-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1246048. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Ultraschall Med. 2011. PMID: 21321841
-
Is it better to use two elastographic methods for liver fibrosis assessment?World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep 7;17(33):3824-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3824. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21987625 Free PMC article.
-
The value of real-time ultrasound elastography in chronic autoimmune thyroiditis.Br J Radiol. 2014 Dec;87(1044):20140604. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140604. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Br J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 25315887 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Meta-analysis: ARFI elastography versus transient elastography for the evaluation of liver fibrosis.Liver Int. 2013 Sep;33(8):1138-47. doi: 10.1111/liv.12240. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Liver Int. 2013. PMID: 23859217 Review.
-
Quantitative Shear Wave Velocity Measurement on Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography for Differential Diagnosis between Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: A Meta-analysis.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015 Dec;41(12):3035-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Sep 12. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26371402 Review.
Cited by
-
Sonographic Elastography of the Thyroid Gland.Pol J Radiol. 2016 Apr 8;81:152-6. doi: 10.12659/PJR.896178. eCollection 2016. Pol J Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27103947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical efficacy of novel elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) for diagnosis of malignant thyroid nodules.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2018 Aug 9;3(4):319-325. doi: 10.1002/lio2.165. eCollection 2018 Aug. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 30186965 Free PMC article.
-
Principles of ultrasound elastography.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018 Apr;43(4):773-785. doi: 10.1007/s00261-018-1475-6. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018. PMID: 29487968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Normal Thyroid Tissue and Autoimmune Thyroiditis in Children Using Shear Wave Elastography.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2019 May 28;11(2):132-139. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2018.2018.0137. Epub 2018 Oct 23. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30362325 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Diagnosis Progress of Ultrasound Imaging Technology in Thyroid Diffuse Diseases.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 13;13(4):700. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13040700. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36832188 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nightingale K, Soo MS, Nightingale R, Trahey G. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging: in vivo demonstration of clinical feasibility. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2002;28:227–235. - PubMed
-
- Ziol M, Handra-Luca A, Kettaneh A, Christidis C, Mal F, Kazemi F, de Lédinghen V, Marcellin P, Dhumeaux D, Trinchet JC, et al. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis by measurement of stiffness in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2005;41:48–54. - PubMed
-
- Castéra L, Vergniol J, Foucher J, Le Bail B, Chanteloup E, Haaser M, Darriet M, Couzigou P, De Lédinghen V. Prospective comparison of transient elastography, Fibrotest, APRI, and liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:343–350. - PubMed
-
- Afdhal N. Debate: Are non-invasive tests ready to replace liver biopsy. favor of the use of non-invasive tests. Clinical Care Options. 2006:7–19.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

