Peptidomics approach to elucidate the proteolytic regulation of bioactive peptides
- PMID: 22586115
- PMCID: PMC3365226
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1203195109
Peptidomics approach to elucidate the proteolytic regulation of bioactive peptides
Abstract
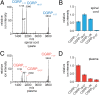
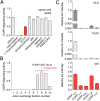
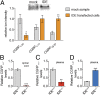
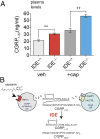
Peptide hormones and neuropeptides have important roles in physiology and therefore the regulation of these bioactive peptides is of great interest. In some cases proteolysis controls the concentrations and signaling of bioactive peptides, and the peptidases that mediate this biochemistry have proven to be extremely successful drug targets. Due to the lack of any general method to identify these peptidases, however, the role of proteolysis in the regulation of most neuropeptides and peptide hormones is unknown. This limitation prompted us to develop an advanced peptidomics-based strategy to identify the peptidases responsible for the proteolysis of significant bioactive peptides. The application of this approach to calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), a neuropeptide associated with blood pressure and migraine, revealed the endogenous CGRP cleavage sites. This information was then used to biochemically purify the peptidase capable of proteolysis of CGRP at those cleavage sites, which led to the identification of insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) as a candidate CGRP-degrading enzyme. CGRP had not been identified as an IDE substrate before and we tested the physiological relevance of this interaction by quantitative measurements of CGRP using IDE null (IDE(-/-)) mice. In the absence of IDE, full-length CGRP levels are elevated in vivo, confirming IDE as an endogenous CGRP-degrading enzyme. By linking CGRP and IDE, this strategy uncovers a previously unknown pathway for CGRP regulation and characterizes an additional role for IDE. More generally, this work suggests that this may be an effective general strategy for characterizing these pathways and peptidases moving forward.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peptidomics methods for the identification of peptidase-substrate interactions.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013 Feb;17(1):83-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.10.038. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23332665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the proteolysis of bioactive peptides using a peptidomics approach.Nat Protoc. 2013 Sep;8(9):1730-42. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.104. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Nat Protoc. 2013. PMID: 23949379 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for the recognition and cleavages of IGF-II, TGF-alpha, and amylin by human insulin-degrading enzyme.J Mol Biol. 2010 Jan 15;395(2):430-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.10.072. Epub 2009 Nov 5. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 19896952 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of Alzheimer's Amyloid-β by a Catalytically Inactive Insulin-Degrading Enzyme.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jun 25;433(13):166993. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166993. Epub 2021 Apr 16. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33865867 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating endogenous peptides and peptidases using peptidomics.Biochemistry. 2011 Sep 6;50(35):7447-61. doi: 10.1021/bi200417k. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21786763 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conformational states and recognition of amyloidogenic peptides of human insulin-degrading enzyme.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 20;110(34):13827-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304575110. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23922390 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidomics methods for the identification of peptidase-substrate interactions.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013 Feb;17(1):83-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.10.038. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23332665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the proteolysis of bioactive peptides using a peptidomics approach.Nat Protoc. 2013 Sep;8(9):1730-42. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.104. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Nat Protoc. 2013. PMID: 23949379 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolysis controls endogenous substance P levels.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 19;8(7):e68638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068638. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23894327 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-diabetic activity of insulin-degrading enzyme inhibitors mediated by multiple hormones.Nature. 2014 Jul 3;511(7507):94-8. doi: 10.1038/nature13297. Epub 2014 May 21. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24847884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hökfelt T, Bartfai T, Bloom F. Neuropeptides: Opportunities for drug discovery. Lancet Neurol. 2003;2:463–472. - PubMed
-
- De Felipe C, et al. Altered nociception, analgesia and aggression in mice lacking the receptor for substance P. Nature. 1998;392:394–397. - PubMed
-
- Patchett AA, et al. A new class of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Nature. 1980;288:280–283. - PubMed
-
- Woods SC, Seeley RJ, Porte D, Jr, Schwartz MW. Signals that regulate food intake and energy homeostasis. Science. 1998;280:1378–1383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

