Protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 (PIAS3) protein promotes SUMOylation and nuclear sequestration of the intracellular domain of ErbB4 protein
- PMID: 22584572
- PMCID: PMC3391121
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.335927
Protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 (PIAS3) protein promotes SUMOylation and nuclear sequestration of the intracellular domain of ErbB4 protein
Abstract
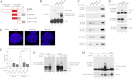
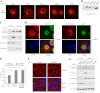
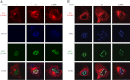
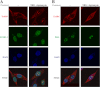
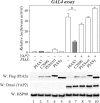
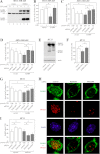
ErbB4 is a receptor tyrosine kinase implicated in the development and homeostasis of the heart, central nervous system, and mammary gland. Cleavable isoforms of ErbB4 release a soluble intracellular domain (ICD) that can translocate to the nucleus and function as a transcriptional coregulator. In search of regulatory mechanisms of ErbB4 ICD function, we identified PIAS3 as a novel interaction partner of ErbB4 ICD. In keeping with the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) E3 ligase function of protein inhibitor of activated STAT (PIAS) proteins, we showed that the ErbB4 ICD is modified by SUMO, and that PIAS3 stimulates the SUMOylation. Upon overexpression of PIAS3, the ErbB4 ICD generated from the full-length receptor accumulated into the nucleus in a manner that was dependent on the functional nuclear localization signal of ErbB4. In the nucleus, ErbB4 colocalized with PIAS3 and SUMO-1 in promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies, nuclear domains involved in regulation of transcription. Accordingly, PIAS3 overexpression had an effect on the transcriptional coregulatory activity of ErbB4, repressing its ability to coactivate transcription with Yes-associated protein. Finally, knockdown of PIAS3 with siRNA partially rescued the inhibitory effect of the ErbB4 ICD on differentiation of MDA-MB-468 breast cancer and HC11 mammary epithelial cells. Our findings illustrate that PIAS3 is a novel regulator of ErbB4 receptor tyrosine kinase, controlling its nuclear sequestration and function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SUMOylation regulates nuclear accumulation and signaling activity of the soluble intracellular domain of the ErbB4 receptor tyrosine kinase.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 1;292(48):19890-19904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.794271. Epub 2017 Oct 3. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28974580 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus E4-ORF3 Targets PIAS3 and Together with E1B-55K Remodels SUMO Interactions in the Nucleus and at Virus Genome Replication Domains.J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10260-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01091-15. Epub 2015 Jul 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26223632 Free PMC article.
-
In situ SUMOylation analysis reveals a modulatory role of RanBP2 in the nuclear rim and PML bodies.Exp Cell Res. 2006 May 1;312(8):1418-30. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.01.013. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16688858
-
SUMO weighs in on a photoreceptor finish.Dev Cell. 2009 Feb;16(2):165-6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.01.017. Dev Cell. 2009. PMID: 19217419 Review.
-
The SUMO pathway in pancreatic cancer: insights and inhibition.Br J Cancer. 2021 Feb;124(3):531-538. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-01119-6. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Br J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33071285 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Monoallelic loss of tumor suppressor GRIM-19 promotes tumorigenesis in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Nov 5;110(45):E4213-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303760110. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24145455 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of protein inhibitor of activated STAT 4, a novel host interacting partner that involved in bovine viral diarrhea virus growth.Virol J. 2020 Apr 22;17(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01330-0. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32321515 Free PMC article.
-
STAT5b is a key effector of NRG-1/ERBB4-mediated myocardial growth.EMBO Rep. 2023 May 4;24(5):e56689. doi: 10.15252/embr.202256689. Epub 2023 Apr 3. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37009825 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-secretase-dependent signaling of receptor tyrosine kinases.Oncogene. 2019 Jan;38(2):151-163. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0465-z. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 30166589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein posttranslational modifications in health and diseases: Functions, regulatory mechanisms, and therapeutic implications.MedComm (2020). 2023 May 2;4(3):e261. doi: 10.1002/mco2.261. eCollection 2023 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37143582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hynes N. E., Lane H. A. (2005) ERBB receptors and cancer. The complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 341–354 - PubMed
-
- Elenius K., Corfas G., Paul S., Choi C. J., Rio C., Plowman G. D., Klagsbrun M. (1997) A novel juxtamembrane domain isoform of HER4/ErbB4. Isoform-specific tissue distribution and differential processing in response to phorbol ester. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 26761–26768 - PubMed
-
- Elenius K., Choi C. J., Paul S., Santiestevan E., Nishi E., Klagsbrun M. (1999) Characterization of a naturally occurring ErbB4 isoform that does not bind or activate phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase. Oncogene 18, 2607–2615 - PubMed
-
- Rio C., Buxbaum J. D., Peschon J. J., Corfas G. (2000) Tumor necrosis factor α-converting enzyme is required for cleavage of erbB4/HER4. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 10379–10387 - PubMed
-
- Ni C. Y., Murphy M. P., Golde T. E., Carpenter G. (2001) γ-Secretase cleavage and nuclear localization of ErbB-4 receptor tyrosine kinase. Science 294, 2179–2181 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

