PPARα as a Transcriptional Regulator for Detoxification of Plant Diet-Derived Unfavorable Compounds
- PMID: 22577367
- PMCID: PMC3345252
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/814945
PPARα as a Transcriptional Regulator for Detoxification of Plant Diet-Derived Unfavorable Compounds
Abstract
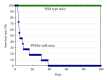
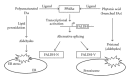
Plants contain potentially toxic compounds for animals and animals have developed physiological strategies to detoxify the ingested toxins during evolution. Feeding mice with various plant seeds and grains showed unexpected result that only sesame killed PPARα-null mice but not wild-type mice at all. A detailed analysis of this observation revealed that PPARα is involved in the metabolism of toxic compounds from plants as well as endobiotic substrates by inducing phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes. PPARα plays a vital role in direct or indirect activation of the relevant genes via the complex network among other xenobiotic nuclear receptors. Thus, PPARα plays its wider and more extensive role in energy metabolism from natural food intake to fat storage than previously thought.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha plays a vital role in inducing a detoxification system against plant compounds with crosstalk with other xenobiotic nuclear receptors.FEBS J. 2006 Jan;273(2):292-300. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.05060.x. FEBS J. 2006. PMID: 16403017
-
Safety and nutritional assessment of GM plants and derived food and feed: the role of animal feeding trials.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Mar;46 Suppl 1:S2-70. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.02.008. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18328408 Review.
-
Genomic and non-genomic interactions of PPARalpha with xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Sep;15(7):324-30. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2004.07.007. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15350604 Review.
-
Novel aspects of PPARalpha-mediated regulation of lipid and xenobiotic metabolism revealed through a nutrigenomic study.Hepatology. 2007 Mar;45(3):767-77. doi: 10.1002/hep.21510. Hepatology. 2007. PMID: 17326203
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha mediates the adaptive response to fasting.J Clin Invest. 1999 Jun;103(11):1489-98. doi: 10.1172/JCI6223. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10359558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fowler ME. Plant poisoning in free-living wild animals: a review. Journal of Wildlife Diseases. 1983;19(1):34–43. - PubMed
-
- Owens JB. Genetic aspects of appetite and food choice in animals. The Journal of Agricultural Science. 1992;119(2):151–155.
-
- Mitchell DY, Petersen DR. Oxidation of aldehydic products of lipid peroxidation by rat liver microsomal aldehyde dehydrogenase. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 1989;269(1):11–17. - PubMed
-
- Rizzo WB, Heinz E, Simon M, Craft DA. Microsomal fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidation of aliphatic aldehyde derived from ether glycerolipid catabolism: implications for Sjogren-Larsson syndrome. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2000;1535(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Willemsen MA, Rotteveel JJ, de Jong JG, et al. Defective metabolism of leukotriene B4 in the Sjogren-Larsson syndrome. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 2001;183(1):61–67. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

