Signaling to cardiac hypertrophy: insights from human and mouse RASopathies
- PMID: 22576369
- PMCID: PMC3459479
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00512
Signaling to cardiac hypertrophy: insights from human and mouse RASopathies
Abstract
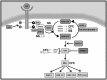
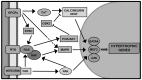
Cardiac hypertrophy is the heart's response to a variety of extrinsic and intrinsic stimuli, some of which might finally lead up to a maladaptive state. An integral part of the pathogenesis of the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy disease (HCM) is the activation of the rat sarcoma (RAS)/RAF/MEK (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase)/MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) cascade. Therefore, the molecular signaling involving RAS has been the subject of intense research efforts, particularly after the identification of the RASopathies. These constitute a class of developmental disorders caused by germline mutations affecting proteins contributing to the RAS pathway. Among other phenotypic features, a subset of these syndromes is characterized by HCM, prompting researchers and clinicians to delve into the chief signaling constituents of cardiac hypertrophy. In this review, we summarize current advances in the knowledge of the molecular signaling events involved in the pathogenesis of cardiac hypertrophy through work completed on patients and on genetically manipulated animals with HCM and RASopathies. Important insights are drawn from the recognition of parallels between cardiac hypertrophy and cancer. Future research promises to further elucidate the complex molecular interactions responsible for cardiac hypertrophy, possibly pointing the way for the identification of new specific targets for the treatment of HCM.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiac Phenotype and Gene Mutations in RASopathies.Genes (Basel). 2024 Aug 2;15(8):1015. doi: 10.3390/genes15081015. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAS signaling pathway mutations and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: getting into and out of the thick of it.J Clin Invest. 2011 Mar;121(3):844-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI46399. Epub 2011 Feb 21. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21339640 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and mutation profile of pediatric patients with RASopathy-associated hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: results from a Chinese cohort.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2019 Feb 7;14(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13023-019-1010-z. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2019. PMID: 30732632 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomous and Non-autonomous Defects Underlie Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in BRAF-Mutant hiPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes.Stem Cell Reports. 2016 Sep 13;7(3):355-369. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.07.018. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Stem Cell Reports. 2016. PMID: 27569062 Free PMC article.
-
Mosaic RASopathies.Cell Cycle. 2013 Jan 1;12(1):43-50. doi: 10.4161/cc.23108. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23255105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sigma-1 Receptor Signaling: In Search of New Therapeutic Alternatives for Cardiovascular and Renal Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 19;24(3):1997. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031997. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inside the Noonan "universe": Literature review on growth, GH/IGF axis and rhGH treatment: Facts and concerns.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 18;13:951331. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.951331. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36060964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERK: A Key Player in the Pathophysiology of Cardiac Hypertrophy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 1;20(9):2164. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092164. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31052420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to Steer and Control ERK and the ERK Signaling Cascade Exemplified by Looking at Cardiac Insufficiency.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 2;20(9):2179. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092179. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31052520 Free PMC article.
-
What Causes Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?Am J Cardiol. 2022 Sep 15;179:74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2022.06.017. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Am J Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35843734 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shih TY, Papageorge AG, Stokes PE, Weeks MO, Scolnick EM. Guanine nucleotide-binding and autophosphorylating activities associated with the p21src protein of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Nature. 1980;287:686–91. - PubMed
-
- Raman M, Chen W, Cobb MH. Differential regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene. 2007;26:3100–12. - PubMed
-
- Yoon S, Seger R. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase: multiple substrates regulate diverse cellular functions. Growth Factors. 2006;24:21–44. - PubMed
-
- Hill JA, Olson EN. Mechanisms of disease: cardiac plasticity. New Engl J Med. 2008;358:1370–80. - PubMed
-
- Takai Y, Sasaki T, Matozaki T. Small GTP-binding proteins. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:153–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

