The Tlo proteins are stoichiometric components of Candida albicans mediator anchored via the Med3 subunit
- PMID: 22562472
- PMCID: PMC3416505
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00095-12
The Tlo proteins are stoichiometric components of Candida albicans mediator anchored via the Med3 subunit
Abstract
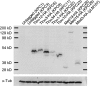
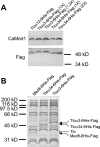
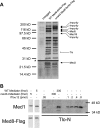
The amplification of the TLO (for telomere-associated) genes in Candida albicans, compared to its less pathogenic, close relative Candida dubliniensis, suggests a role in virulence. Little, however, is known about the function of the Tlo proteins. We have purified the Mediator coactivator complex from C. albicans (caMediator) and found that Tlo proteins are a stoichiometric component of caMediator. Many members of the Tlo family are expressed, and each is a unique member of caMediator. Protein expression analysis of individual Tlo proteins, as well as the purification of tagged Tlo proteins, demonstrate that there is a large free population of Tlo proteins in addition to the Mediator-associated population. Coexpression and copurification of Tloα12 and caMed3 in Escherichia coli established a direct physical interaction between the two proteins. We have also made a C. albicans med3Δ/Δ strain and purified an intact Mediator from this strain. The analysis of the composition of the med3Δ Mediator shows that it lacks a Tlo subunit. Regarding Mediator function, the med3Δ/Δ strain serves as a substitute for the difficult-to-make tloΔ/Δ C. albicans strain. A potential role of the TLO and MED3 genes in virulence is supported by the inability of the med3Δ/Δ strain to form normal germ tubes. This study of caMediator structure provides initial clues to the mechanism of action of the Tlo genes and a platform for further mechanistic studies of caMediator's involvement in gene regulatory patterns that underlie pathogenesis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of Mediator in virulence and antifungal drug resistance in pathogenic fungi.Curr Genet. 2019 Jun;65(3):621-630. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00932-8. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30637479 Review.
-
The role of the Mediator complex in fungal pathogenesis and response to antifungal agents.Essays Biochem. 2023 Sep 13;67(5):843-851. doi: 10.1042/EBC20220238. Essays Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37013399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amplification of TLO Mediator Subunit Genes Facilitate Filamentous Growth in Candida Spp.PLoS Genet. 2016 Oct 14;12(10):e1006373. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006373. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27741243 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion of the TLO gene family enhances the virulence of Candida species.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 20;13(7):e0200852. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200852. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30028853 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the Candida albicans TLO gene family using CRISPR-Cas9 mutagenesis allows characterisation of functional differences in α-, β- and γ- TLO gene function.PLoS Genet. 2023 Dec 4;19(12):e1011082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011082. eCollection 2023 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 38048294 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of Mediator in virulence and antifungal drug resistance in pathogenic fungi.Curr Genet. 2019 Jun;65(3):621-630. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00932-8. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30637479 Review.
-
The role of the Mediator complex in fungal pathogenesis and response to antifungal agents.Essays Biochem. 2023 Sep 13;67(5):843-851. doi: 10.1042/EBC20220238. Essays Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37013399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Candida pathogenic species complex.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014 Sep 2;4(9):a019778. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a019778. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014. PMID: 25183855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Budding off: bringing functional genomics to Candida albicans.Brief Funct Genomics. 2016 Mar;15(2):85-94. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elv035. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Brief Funct Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26424829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fungal mediator tail subunits contain classical transcriptional activation domains.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Apr;35(8):1363-75. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01508-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25645928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baidoobonso SM, Guidi BW, Myers LC. 2007. Med19(Rox3) regulates intermodule interactions in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae mediator complex. J. Biol. Chem. 282:5551–5559 - PubMed
-
- Béve J, et al. 2005. The structural and functional role of Med5 in the yeast Mediator tail module. J. Biol. Chem. 280:41366–41372 - PubMed
-
- Bjorklund S, Gustafsson CM. 2005. The yeast Mediator complex and its regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 30:240–244 - PubMed
-
- Borggrefe T, Davis R, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Kornberg RD. 2002. A complex of the Srb8, -9, -10 and -11 transcriptional regulatory proteins from yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 277:44202–44207 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

