New evidence on α-synuclein and Tau binding to conformation and sequence specific GC* rich DNA: Relevance to neurological disorders
- PMID: 22557921
- PMCID: PMC3341714
- DOI: 10.4103/0975-7406.94811
New evidence on α-synuclein and Tau binding to conformation and sequence specific GC* rich DNA: Relevance to neurological disorders
Abstract
Background: Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) topology plays a critical role in maintaining the integrity of the genome and cellular functions. Although changes in DNA conformation and structural dynamics in the brain have been associated with various neurological disorders, its precise role in the pathogenesis is still unclear. Previous studies from our laboratory have shown that there is a conformational change in the genomic DNA of Parkinson's disease (PD) (B to altered B-DNA) and Alzheimer's disease brain (B to Z-DNA). However, there is limited information on the mechanism on DNA dynamics changes in brain.
Objective: In the present study, we have investigated the DNA conformation and sequence specific binding ability of α-Synuclein and Tau with reference to B-DNA and Z-DNA using oligonucleotide (CGCGCGCG)(2) as a novel model DNA system. This sequence is predominantly present in the promoter region of the genes of biological relevance.
Materials and methods: Natively, (CGCGCGCG)(2) sequence exists in B-DNA conformation, but in the presence of high sodium concentration (4 M NaCl), the oligo converts into Z-DNA form. We used circular dichroism, melting temperature and fluorescence studies to understand protein-DNA interactions.
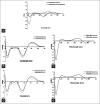
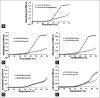
Results: CD studies indicated that both α-Synuclein and Tau bind to B-DNA conformation of (CGCGCGCG)(2) and induce altered B-form. Further, these proteins increased the melting temperature and decreased the number of EtBr molecules bound per base pair of DNA in B-form indicating that DNA stability is favored to alter B-DNA conformation, which could be an intermediate form favoring Z-DNA conformation. Moreover, both α-Synuclein and Tau also bound to disease-linked Z-DNA conformation of (CGCGCGCG)(2) and further stabilized the Z-conformation.
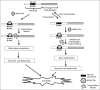
Conclusions: The present study provides vital mechanistic information on Synuclein and Tau binding to DNA in a conformation-specific manner causing conformational transition. Furthermore, both the proteins stabilize Z-DNA conformation. These have altered minor and major groove patterns and thus may have significant biological implications in relevance to gene expression pattern in neurodegeneration. We discuss the implications of α-Synuclein/Tau binding to DNA and stabilizing the altered conformations of DNA in neuronal cell dysfunction.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Parkinson's disease; Tau; Z-DNA; oligonucleotide-protein interaction; α-Synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of advanced glycation on aggregation and DNA binding properties of α-synuclein.J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;24 Suppl 2:211-21. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-101965. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011. PMID: 21441659 Review.
-
The direct and indirect effects of α-synuclein on microtubule stability in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2018 Jun 27;14:1685-1695. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S166322. eCollection 2018. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2018. PMID: 29983568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Amyloid Switch Triggered by Early Heterotypic Oligomerization of Intrinsically Disordered α-Synuclein and Tau.J Mol Biol. 2018 Aug 3;430(16):2508-2520. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.04.020. Epub 2018 Apr 25. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29704492
-
DNA induces folding in alpha-synuclein: understanding the mechanism using chaperone property of osmolytes.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007 Aug 1;464(1):57-69. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2007.03.042. Epub 2007 Apr 26. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007. PMID: 17537399
-
α-Synuclein and tau concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of patients presenting with parkinsonism: a cohort study.Lancet Neurol. 2011 Mar;10(3):230-40. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70014-X. Lancet Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21317042
Cited by
-
Synucleins and Gene Expression: Ramblers in a Crowd or Cops Regulating Traffic?Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Jul 13;10:224. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00224. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28751856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear localization of alpha-synuclein affects the cognitive and motor behavior of mice by inducing DNA damage and abnormal cell cycle of hippocampal neurons.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Nov 10;15:1015881. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1015881. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36438187 Free PMC article.
-
(Dys)functional insights into nucleic acids and RNA-binding proteins modulation of the prion protein and α-synuclein phase separation.Biophys Rev. 2023 Jun 6;15(4):577-589. doi: 10.1007/s12551-023-01067-4. eCollection 2023 Aug. Biophys Rev. 2023. PMID: 37681103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mini review: linkage between α-Synuclein protein and cognition.Transl Neurodegener. 2015 Mar 28;4:5. doi: 10.1186/s40035-015-0026-0. eCollection 2015. Transl Neurodegener. 2015. PMID: 25834729 Free PMC article.
-
ATP13A2 and Alpha-synuclein: a Metal Taste in Autophagy.Exp Neurobiol. 2014 Dec;23(4):314-23. doi: 10.5607/en.2014.23.4.314. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Exp Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 25548531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rich A. DNA comes in many forms. Gene. 1993;135:99–109. - PubMed
-
- Bacolla A, Wells RD. Non-B DNA conformations as determinants of mutagenesis and human disease. Mol Carcinog. 2009;48:273–85. - PubMed
-
- Hegde ML, Vasudevaraju P, Rao KJ. DNA induced folding/fibrillation of alpha-synuclein: New insights in Parkinson's disease. Front Biosci. 2010;15:418–36. - PubMed
-
- Vasudevaraju P, Bharathi, Garruto RM, Sambamurti K, Rao KS. Role of DNA dynamics in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res Rev. 2008;58:136–48. - PubMed
-
- Hegde ML, Gupta VB, Anitha M, Harikrishna T, Shankar SK, Muthane U, et al. Studies on genomic DNA topology and stability in brain regions of Parkinson's disease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2006;449:143–56. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

