Functional cooperation between human adenovirus type 5 early region 4, open reading frame 6 protein, and cellular homeobox protein HoxB7
- PMID: 22553335
- PMCID: PMC3421667
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00222-12
Functional cooperation between human adenovirus type 5 early region 4, open reading frame 6 protein, and cellular homeobox protein HoxB7
Abstract
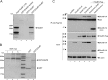
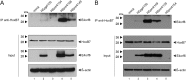
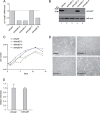
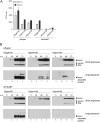
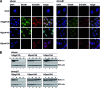
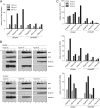
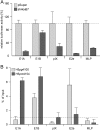
Human adenovirus type 5 (HAdV5) E4orf6 (early region 4 open reading frame 6 protein) is a multifunctional early viral protein promoting efficient replication and progeny production. E4orf6 complexes with E1B-55K to assemble cellular proteins into a functional E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that not only mediates proteasomal degradation of host cell substrates but also facilitates export of viral late mRNA to promote efficient viral protein expression and host cell shutoff. Recent findings defined the role of E4orf6 in RNA splicing independent of E1B-55K binding. To reveal further functions of the early viral protein in infected cells, we used a yeast two-hybrid system and identified the homeobox transcription factor HoxB7 as a novel E4orf6-associated protein. Using a HoxB7 knockdown cell line, we observed a positive role of HoxB7 in adenoviral replication. Our experiments demonstrate that the absence of HoxB7 leads to inefficient viral progeny production, as HAdV5 gene expression is highly regulated by HoxB7-mediated activation of various adenoviral promoters. We have thus identified a novel role of E4orf6 in HAdV5 gene transcription via regulation of homeobox protein-dependent modulation of viral promoter activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adenovirus ubiquitin-protein ligase stimulates viral late mRNA nuclear export.J Virol. 2007 Jan;81(2):575-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01725-06. Epub 2006 Nov 1. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17079297 Free PMC article.
-
E1B-55K-Mediated Regulation of RNF4 SUMO-Targeted Ubiquitin Ligase Promotes Human Adenovirus Gene Expression.J Virol. 2018 Jun 13;92(13):e00164-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00164-18. Print 2018 Jul 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29695423 Free PMC article.
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase activity associated with the adenoviral E1B-55K-E4orf6 complex does not require CRM1-dependent export.J Virol. 2011 Jul;85(14):7081-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02368-10. Epub 2011 May 11. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21561915 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of mRNA production by the adenoviral E1B 55-kDa and E4 Orf6 proteins.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003;272:287-330. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-05597-7_10. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12747554 Review.
-
The biology of the adenovirus E1B 55K protein.FEBS Lett. 2019 Dec;593(24):3504-3517. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13694. Epub 2019 Dec 8. FEBS Lett. 2019. PMID: 31769868 Review.
Cited by
-
Amino acid exchanges in the putative nuclear export signal of adenovirus type 5 L4-100K severely reduce viral progeny due to effects on hexon biogenesis.J Virol. 2013 Feb;87(3):1893-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02061-12. Epub 2012 Nov 21. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23175361 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular SUMO-specific proteases regulate HAdV-C5 E1B-55K SUMOylation and virus-induced cell transformation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 27;14:1484241. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1484241. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39397864 Free PMC article.
-
The adenoviral oncogene E1A-13S interacts with a specific isoform of the tumor suppressor PML to enhance viral transcription.J Virol. 2013 Jan;87(2):965-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02023-12. Epub 2012 Nov 7. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23135708 Free PMC article.
-
Sp100 isoform-specific regulation of human adenovirus 5 gene expression.J Virol. 2014 Jun;88(11):6076-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00469-14. Epub 2014 Mar 12. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24623443 Free PMC article.
-
Sp100A is a tumor suppressor that activates p53-dependent transcription and counteracts E1A/E1B-55K-mediated transformation.Oncogene. 2016 Jun 16;35(24):3178-89. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.378. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26477309
References
-
- Abate-Shen C. 2002. Deregulated homeobox gene expression in cancer: cause or consequence? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2:777–785 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

