PI3-kinase/Akt pathway-regulated membrane insertion of acid-sensing ion channel 1a underlies BDNF-induced pain hypersensitivity
- PMID: 22553040
- PMCID: PMC6622133
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4479-11.2012
PI3-kinase/Akt pathway-regulated membrane insertion of acid-sensing ion channel 1a underlies BDNF-induced pain hypersensitivity
Abstract
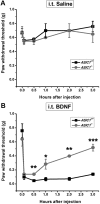
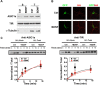
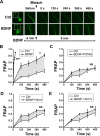
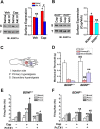
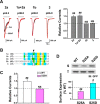
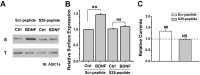
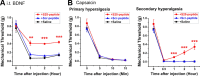
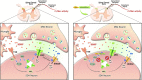
Central neural plasticity plays a key role in pain hypersensitivity. This process is modulated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and also involves the type 1a acid-sensing ion channel (ASIC1a). However, the interactions between the BDNF receptor, tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB), and ASIC1a are unclear. Here, we show that deletion of ASIC1 gene suppressed the sustained mechanical hyperalgesia induced by intrathecal BDNF application in mice. In both rat spinal dorsal horn neurons and heterologous cell cultures, the BDNF/TrkB pathway enhanced ASIC1a currents via phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) cascade and phosphorylation of cytoplasmic residue Ser-25 of ASIC1a, resulting in enhanced forward trafficking and increased surface expression. Moreover, in both rats and mice, this enhanced ASIC1a activity was required for BDNF-mediated hypersensitivity of spinal dorsal horn nociceptive neurons and central mechanical hyperalgesia, a process that was abolished by intrathecal application of a peptide representing the N-terminal region of ASIC1a encompassing Ser-25. Thus, our results reveal a novel mechanism underlying central sensitization and pain hypersensitivity, and reinforce the critical role of ASIC1a channels in these processes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PI3-kinase/Akt pathway-regulated membrane transportation of acid-sensing ion channel 1a/Calcium ion influx/endoplasmic reticulum stress activation on PDGF-induced HSC Activation.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Jun;23(6):3940-3950. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14275. Epub 2019 Apr 2. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30938088 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of acid-sensing ion channel ASIC1a in spinal dorsal horn neurons contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity.J Neurosci. 2007 Oct 10;27(41):11139-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3364-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17928456 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF Contributes to Spinal Long-Term Potentiation and Mechanical Hypersensitivity Via Fyn-Mediated Phosphorylation of NMDA Receptor GluN2B Subunit at Tyrosine 1472 in Rats Following Spinal Nerve Ligation.Neurochem Res. 2017 Oct;42(10):2712-2729. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2274-0. Epub 2017 May 11. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28497343
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulation of T-type Ca2+ channels in sensory neurons contributes to increased peripheral pain sensitivity.Sci Signal. 2019 Sep 24;12(600):eaaw2300. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaw2300. Sci Signal. 2019. PMID: 31551295
-
Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Promotes Growth of Neurons and Neural Stem Cells Possibly by Triggering the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/ AKT/Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β/β-catenin Pathway.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017;16(7):828-836. doi: 10.2174/1871527316666170518170422. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 28524001
Cited by
-
Maternal Creatine Supplementation Positively Affects Male Rat Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Adult Offspring.Nutrients. 2019 Aug 27;11(9):2014. doi: 10.3390/nu11092014. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31461895 Free PMC article.
-
Factors and Molecular Mechanisms Influencing the Protein Synthesis, Degradation and Membrane Trafficking of ASIC1a.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 23;8:596304. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.596304. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33195276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular ASIC1a regulates mitochondrial permeability transition-dependent neuronal death.Cell Death Differ. 2013 Oct;20(10):1359-69. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.90. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Cell Death Differ. 2013. PMID: 23852371 Free PMC article.
-
ASICs as therapeutic targets for migraine.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Jul;94:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.12.015. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25582295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs): therapeutic targets for neurological diseases and their regulation.BMB Rep. 2013 Jun;46(6):295-304. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2013.46.6.121. BMB Rep. 2013. PMID: 23790972 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adelson DW, Wei JY, Kruger L. Warm-sensitive afferent splanchnic C-fiber units in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1997;77:2989–3002. - PubMed
-
- Benson CJ, Eckert SP, McCleskey EW. Acid-evoked currents in cardiac sensory neurons: a possible mediator of myocardial ischemic sensation. Circ Res. 1999;84:921–928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

