A unifying model for mTORC1-mediated regulation of mRNA translation
- PMID: 22552098
- PMCID: PMC3347774
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11083
A unifying model for mTORC1-mediated regulation of mRNA translation
Abstract
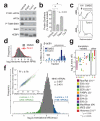
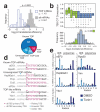
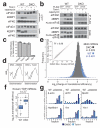
The mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) kinase nucleates a pathway that promotes cell growth and proliferation and is the target of rapamycin, a drug with many clinical uses. mTORC1 regulates messenger RNA translation, but the overall translational program is poorly defined and no unifying model exists to explain how mTORC1 differentially controls the translation of specific mRNAs. Here we use high-resolution transcriptome-scale ribosome profiling to monitor translation in mouse cells acutely treated with the mTOR inhibitor Torin 1, which, unlike rapamycin, fully inhibits mTORC1 (ref. 2). Our data reveal a surprisingly simple model of the mRNA features and mechanisms that confer mTORC1-dependent translation control. The subset of mRNAs that are specifically regulated by mTORC1 consists almost entirely of transcripts with established 5' terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) motifs, or, like Hsp90ab1 and Ybx1, with previously unrecognized TOP or related TOP-like motifs that we identified. We find no evidence to support proposals that mTORC1 preferentially regulates mRNAs with increased 5' untranslated region length or complexity. mTORC1 phosphorylates a myriad of translational regulators, but how it controls TOP mRNA translation is unknown. Remarkably, loss of just the 4E-BP family of translational repressors, arguably the best characterized mTORC1 substrates, is sufficient to render TOP and TOP-like mRNA translation resistant to Torin 1. The 4E-BPs inhibit translation initiation by interfering with the interaction between the cap-binding protein eIF4E and eIF4G1. Loss of this interaction diminishes the capacity of eIF4E to bind TOP and TOP-like mRNAs much more than other mRNAs, explaining why mTOR inhibition selectively suppresses their translation. Our results clarify the translational program controlled by mTORC1 and identify 4E-BPs and eIF4G1 as its master effectors.
Figures

Comment in
-
Cancer biology: The director's cut.Nature. 2012 May 2;485(7396):50-1. doi: 10.1038/485050a. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22552093 No abstract available.
-
Re: A unifying model for mTORC1-mediated regulation of mRNA translation.J Urol. 2012 Dec;188(6):2433-4. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.08.066. Epub 2012 Oct 22. J Urol. 2012. PMID: 23141279 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
La-related Protein 1 (LARP1) Represses Terminal Oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNA Translation Downstream of mTOR Complex 1 (mTORC1).J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 26;290(26):15996-6020. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.621730. Epub 2015 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25940091 Free PMC article.
-
Role of p70S6K1-mediated phosphorylation of eIF4B and PDCD4 proteins in the regulation of protein synthesis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 14;287(51):42890-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.404822. Epub 2012 Oct 26. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23105104 Free PMC article.
-
Stable isotope-labelling analysis of the impact of inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin on protein synthesis.Biochem J. 2012 May 15;444(1):141-51. doi: 10.1042/BJ20112107. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22428559
-
Translational control of mRNAs by 3'-Untranslated region binding proteins.BMB Rep. 2017 Apr;50(4):194-200. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.4.040. BMB Rep. 2017. PMID: 28287067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTOR-sensitive translation: Cleared fog reveals more trees.RNA Biol. 2017 Oct 3;14(10):1299-1305. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1290041. Epub 2017 Feb 10. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28277937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disease: Disturbing the balance between phase separation and irreversible aggregation.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2020;174:187-223. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2020.04.021. Epub 2020 May 12. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 32828466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robust single-cell discovery of RNA targets of RNA-binding proteins and ribosomes.Nat Methods. 2021 May;18(5):507-519. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01128-0. Epub 2021 May 7. Nat Methods. 2021. PMID: 33963355 Free PMC article.
-
GWIPS-viz as a tool for exploring ribosome profiling evidence supporting the synthesis of alternative proteoforms.Proteomics. 2015 Jul;15(14):2410-6. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400603. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25736862 Free PMC article.
-
Translation of Tudor-SN, a novel terminal oligo-pyrimidine (TOP) mRNA, is regulated by the mTORC1 pathway in cardiomyocytes.RNA Biol. 2021 Jun;18(6):900-913. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1827783. Epub 2020 Oct 15. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33054526 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription start site choice diversifies mRNA isoforms and defines cancer cell behavior.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023 Dec;30(12):1840-1841. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01157-7. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 38012420 No abstract available.
References
-
- Moffat J, et al. A lentiviral RNAi library for human and mouse genes applied to an arrayed viral high-content screen. Cell. 2006;124:1283–98. - PubMed
-
- Ali SM, Sabatini DM. Structure of S6 kinase 1 determines whether raptor-mTOR or rictor-mTOR phosphorylates its hydrophobic motif site. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:19445–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

