Functional association between eyegone and HP1a mediates wingless transcriptional repression during development
- PMID: 22547675
- PMCID: PMC3434488
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.06311-11
Functional association between eyegone and HP1a mediates wingless transcriptional repression during development
Abstract
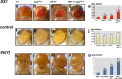
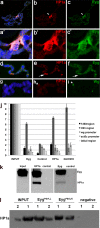
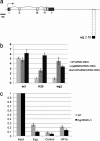
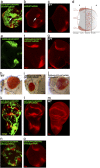
The eyegone (eyg) gene encodes Eyg, a transcription factor of the Pax family with multiple roles during Drosophila development. Although Eyg has been shown to act as a repressor, nothing is known about the mechanism by which it represses its target genes. Here, we show that Eyg forms a protein complex with heterochromatin protein 1a (HP1a). Both proteins bind to the same chromatin regions on polytene chromosomes and act cooperatively to suppress variegation and mediate gene silencing. In addition, Eyg binds to a wingless (wg) enhancer region, recruiting HP1a to assemble a closed, heterochromatin-like conformation that represses transcription of the wg gene. We describe here the evidence that suggests that Eyg, encoded by eyegone (eyg), represses wingless (wg) during eye development by association with HP1a. We show that Eyg forms a protein complex with HP1a and both proteins colocalize on salivary gland polytene chromosomes. Using position effect variegation (PEV) experiments, we demonstrated that eyg has a dose-dependent effect on heterochromatin gene silencing and identified a genetic interaction with HP1a in this process. We further demonstrated that HP1a binds to the same wg enhancer element as Eyg. DNase I sensitivity assays indicated that this enhancer region has a closed heterochromatin-like conformation, which becomes open in eyg mutants. In these mutants, much less HP1a binds to the wg enhancer region, as shown by ChIP experiments. Furthermore, as previously described for Eyg, a reduction in the amount of HP1a in the eye imaginal disc derepresses wg. Together, our results suggest a model in which Eyg specifically binds to the wg enhancer region, recruiting HP1a to that site. The recruitment of HP1a prevents transcription by favoring a closed, heterochromatin-like structure. Thus, for the first time, we show that HP1a plays a direct role in the repression of a developmentally regulated gene, wg, during Drosophila eye development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insights into HP1a-Chromatin Interactions.Cells. 2020 Aug 9;9(8):1866. doi: 10.3390/cells9081866. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32784937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two Pax genes, eye gone and eyeless, act cooperatively in promoting Drosophila eye development.Development. 2003 Jul;130(13):2939-51. doi: 10.1242/dev.00522. Development. 2003. PMID: 12756177
-
The role of eyg Pax gene in the development of the head vertex in Drosophila.Dev Biol. 2010 Jan 15;337(2):246-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.10.038. Epub 2009 Nov 6. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 19896935
-
JAK/STAT signaling promotes regional specification by negatively regulating wingless expression in Drosophila.Development. 2006 Dec;133(23):4721-9. doi: 10.1242/dev.02675. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Development. 2006. PMID: 17079268
-
Powerful Drosophila screens that paved the wingless pathway.Fly (Austin). 2014;8(4):218-25. doi: 10.4161/19336934.2014.985988. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Fly (Austin). 2014. PMID: 25565425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The TALE transcription factor homothorax functions to assemble heterochromatin during Drosophila embryogenesis.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 20;10(3):e0120662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120662. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25794008 Free PMC article.
-
The Paramount Role of Drosophila melanogaster in the Study of Epigenetics: From Simple Phenotypes to Molecular Dissection and Higher-Order Genome Organization.Insects. 2021 Sep 29;12(10):884. doi: 10.3390/insects12100884. Insects. 2021. PMID: 34680653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into HP1a-Chromatin Interactions.Cells. 2020 Aug 9;9(8):1866. doi: 10.3390/cells9081866. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32784937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dampening the signals transduced through hedgehog via microRNA miR-7 facilitates notch-induced tumourigenesis.PLoS Biol. 2013;11(5):e1001554. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001554. Epub 2013 May 7. PLoS Biol. 2013. PMID: 23667323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldaz S, Morata G, Azpiazu N. 2003. The Pax-homeobox gene eyegone is involved in the subdivision of the thorax of Drosophila. Development 130:4473–4482 - PubMed
-
- Chi N, Epstein JA. 2002. Getting your Pax straight: Pax proteins in development and disease. Trends Genet. 18:41–47 - PubMed
-
- Comet I, et al. 2006. PRE-mediated bypass of two Su(Hw) insulators targets PcG proteins to a downstream promoter. Dev. Cell 11:117–124 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
