Genetic and functional characterization of cyclic lipopeptide white-line-inducing principle (WLIP) production by rice rhizosphere isolate Pseudomonas putida RW10S2
- PMID: 22544260
- PMCID: PMC3416372
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00335-12
Genetic and functional characterization of cyclic lipopeptide white-line-inducing principle (WLIP) production by rice rhizosphere isolate Pseudomonas putida RW10S2
Abstract
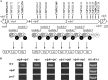
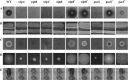
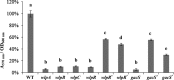
The secondary metabolite mediating the GacS-dependent growth-inhibitory effect exerted by the rice rhizosphere isolate Pseudomonas putida RW10S2 on phytopathogenic Xanthomonas species was identified as white-line-inducing principle (WLIP), a member of the viscosin group of cyclic lipononadepsipeptides. WLIP producers are commonly referred to by the taxonomically invalid name "Pseudomonas reactans," based on their capacity to reveal the presence of a nearby colony of Pseudomonas tolaasii by inducing the formation of a visible precipitate ("white line") in agar medium between both colonies. This phenomenon is attributed to the interaction of WLIP with a cyclic lipopeptide of a distinct structural group, the fungitoxic tolaasin, and has found application as a diagnostic tool to identify tolaasin-producing bacteria pathogenic to mushrooms. The genes encoding the WLIP nonribosomal peptide synthetases WlpA, WlpB, and WlpC were identified in two separate genomic clusters (wlpR-wlpA and wlpBC) with an operon organization similar to that of the viscosin, massetolide, and entolysin biosynthetic systems. Expression of wlpR is dependent on gacS, and the encoded regulator of the LuxR family (WlpR) activates transcription of the biosynthetic genes and the linked export genes, which is not controlled by the RW10S2 quorum-sensing system PmrR/PmrI. In addition to linking the known phenotypes of white line production and hemolytic activity of a WLIP producer with WLIP biosynthesis, additional properties of ecological relevance conferred by WLIP production were identified, namely, antagonism against Xanthomonas and involvement in swarming and biofilm formation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The antimicrobial compound xantholysin defines a new group of Pseudomonas cyclic lipopeptides.PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e62946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062946. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23690965 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct lipopeptide production systems for WLIP (white line-inducing principle) in Pseudomonas fluorescens and Pseudomonas putida.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2013 Feb;5(1):160-9. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12015. Epub 2012 Dec 4. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23757145
-
PCR detection of novel non-ribosomal peptide synthetase genes in lipopeptide-producing Pseudomonas.Microb Ecol. 2011 Nov;62(4):941-7. doi: 10.1007/s00248-011-9885-9. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Microb Ecol. 2011. PMID: 21647696
-
Genetic regulations of the biosynthesis of microbial surfactants: an overview.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2008;25:165-85. doi: 10.5661/bger-25-165. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2008. PMID: 21412355 Review.
-
Diversity of nonribosomal peptide synthetases involved in the biosynthesis of lipopeptide biosurfactants.Int J Mol Sci. 2010 Dec 30;12(1):141-72. doi: 10.3390/ijms12010141. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 21339982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The antimicrobial compound xantholysin defines a new group of Pseudomonas cyclic lipopeptides.PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e62946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062946. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23690965 Free PMC article.
-
Transporter Gene-Mediated Typing for Detection and Genome Mining of Lipopeptide-Producing Pseudomonas.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Jan 25;88(2):e0186921. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01869-21. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34731056 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas putida-a versatile host for the production of natural products.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Aug;99(15):6197-214. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6745-4. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26099332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complete Genome Sequence of the Sugar Cane Endophyte Pseudomonas aurantiaca PB-St2, a Disease-Suppressive Bacterium with Antifungal Activity toward the Plant Pathogen Colletotrichum falcatum.Genome Announc. 2014 Jan 23;2(1):e01108-13. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01108-13. Genome Announc. 2014. PMID: 24459254 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas Lipopeptide-Mediated Biocontrol: Chemotaxonomy and Biological Activity.Molecules. 2022 Jan 7;27(2):372. doi: 10.3390/molecules27020372. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35056688 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akama H, et al. 2004. Crystal structure of the drug discharge outer membrane protein, OprM, of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: dual modes of membrane anchoring and occluded cavity end. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 52816–52819 - PubMed
-
- Balibar CJ, Vaillancourt FH, Walsh CT. 2005. Generation of d amino acid residues in assembly of arthrofactin by dual condensation/epimerization domains. Chem. Biol. 12: 1189–1200 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

