Distinct roles of neuroligin-1 and SynCAM1 in synapse formation and function in primary hippocampal neuronal cultures
- PMID: 22542674
- PMCID: PMC3371159
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.04.047
Distinct roles of neuroligin-1 and SynCAM1 in synapse formation and function in primary hippocampal neuronal cultures
Abstract
Neuroligins are a family of cell adhesion molecules critical in establishing proper central nervous system connectivity; disruption of neuroligin signaling in vivo precipitates a broad range of cognitive deficits. Despite considerable recent progress, the specific synaptic function of neuroligin-1 (NL1) remains unclear. A current model proposes that NL1 acts exclusively to mature pre-existent synaptic connections in an activity-dependent manner. A second element of this activity-dependent maturation model is that an alternate molecule acts upstream of NL1 to initiate synaptic connections. SynCAM1 (SC1) is hypothesized to function in this capacity, though several uncertainties remain regarding SC1 function. Using overexpression and chronic pharmacological blockade of synaptic activity, we now demonstrate that NL1 is capable of robustly recruiting synapsin-positive terminals independent of synaptic maturation and activity in 2-week old primary hippocampal neuronal cultures. We further report that neither SC1 overexpression nor knockdown of endogenous SC1 impacts synapsin punctum densities, suggesting that SC1 is not a limiting factor of synapse initiation in maturing hippocampal neurons in vitro. Consistent with these findings, we observed profoundly greater recruitment of synapsin-positive presynaptic terminals by NL1 than SC1 in a mixed-culture assay of artificial synaptogenesis between primary neurons and heterologous cells. Collectively, our results contend multiple aspects of the proposed model of NL1 and SC1 function and motivate an alternative model whereby SC1 may mature synaptic connections forged by NL1. Supporting this model, we present evidence that combined NL1 and SC1 overexpression triggers excitotoxic neurodegeneration through SC1 signaling at synaptic connections initiated by NL1.
Copyright © 2012 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
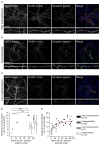
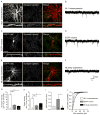
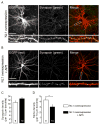

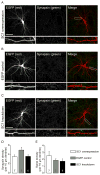
Similar articles
-
Thrombospondin 1 accelerates synaptogenesis in hippocampal neurons through neuroligin 1.Nat Neurosci. 2010 Jan;13(1):22-4. doi: 10.1038/nn.2459. Epub 2009 Nov 15. Nat Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 19915562
-
Unique versus Redundant Functions of Neuroligin Genes in Shaping Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapse Properties.J Neurosci. 2017 Jul 19;37(29):6816-6836. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0125-17.2017. Epub 2017 Jun 12. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28607166 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroligins Are Selectively Essential for NMDAR Signaling in Cerebellar Stellate Interneurons.J Neurosci. 2016 Aug 31;36(35):9070-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1356-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27581450 Free PMC article.
-
Autism-associated mutations in ProSAP2/Shank3 impair synaptic transmission and neurexin-neuroligin-mediated transsynaptic signaling.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 24;32(43):14966-78. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2215-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23100419 Free PMC article.
-
A matter of balance: role of neurexin and neuroligin at the synapse.Neurochem Res. 2013 Jun;38(6):1174-89. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1029-9. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23559421 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroligin 1 modulates striatal glutamatergic neurotransmission in a pathway and NMDAR subunit-specific manner.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2015 Jul 29;7:11. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2015.00011. eCollection 2015. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26283958 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors and Their Impact on Wiring of Brain Synapses.Annu Rev Genet. 2018 Nov 23;52:567-590. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120417-031513. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Annu Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 30212237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redundant Postsynaptic Functions of SynCAMs 1-3 during Synapse Formation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Jan 31;10:24. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00024. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28197078 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal cap-dependent translation regulates presynaptic p35.Dev Neurobiol. 2014 Mar;74(3):351-64. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22154. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Dev Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24254883 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of being Nernst: Synaptic activity and functional relevance in stem cell-derived neurons.World J Stem Cells. 2015 Jul 26;7(6):899-921. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i6.899. World J Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 26240679 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Biederer T, Sara Y, Mozhayeva M, Atasoy D, Liu X, Kavalali ET, Südhof TC. SynCAM, a synaptic adhesion molecule that drives synapse assembly. Science. 2002;297:1525–1531. - PubMed
-
- Biederer T, Scheiffele P. Mixed-culture assays for analyzing neuronal synapse formation. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:670–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

