The proline rich homeodomain protein PRH/Hhex forms stable oligomers that are highly resistant to denaturation
- PMID: 22540015
- PMCID: PMC3335068
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035984
The proline rich homeodomain protein PRH/Hhex forms stable oligomers that are highly resistant to denaturation
Abstract
Background: Many transcription factors control gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences at or near the genes that they regulate. However, some transcription factors play more global roles in the control of gene expression by altering the architecture of sections of chromatin or even the whole genome. The ability to form oligomeric protein assemblies allows many of these proteins to manipulate extensive segments of DNA or chromatin via the formation of structures such as DNA loops or protein-DNA fibres.
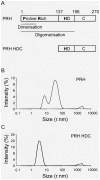
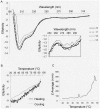
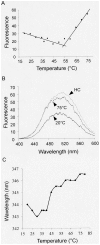
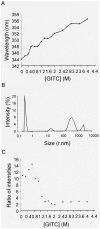
Principal findings: Here we show that the proline rich homeodomain protein PRH/Hhex forms predominantly octameric and/or hexadecameric species in solution as well as larger assemblies. We show that these assemblies are highly stable resisting denaturation by temperature and chemical denaturants.
Conclusion: These data indicate that PRH is functionally and structurally related to the Lrp/AsnC family of proteins, a group of proteins that are known to act globally to control gene expression in bacteria and archaea.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Misregulation of the proline rich homeodomain (PRH/HHEX) protein in cancer cells and its consequences for tumour growth and invasion.Cell Biosci. 2016 Feb 13;6:12. doi: 10.1186/s13578-016-0077-7. eCollection 2016. Cell Biosci. 2016. PMID: 26877867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA compaction by the higher-order assembly of PRH/Hex homeodomain protein oligomers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Nov;38(21):7513-25. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq659. Epub 2010 Jul 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20675722 Free PMC article.
-
DNA wrapping and distortion by an oligomeric homeodomain protein.J Mol Biol. 2008 Oct 31;383(1):10-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.08.004. Epub 2008 Aug 7. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18755198
-
Oligomerisation of the developmental regulator proline rich homeodomain (PRH/Hex) is mediated by a novel proline-rich dimerisation domain.J Mol Biol. 2006 May 12;358(4):943-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.02.020. Epub 2006 Feb 28. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16540119
-
PRH/Hex: an oligomeric transcription factor and multifunctional regulator of cell fate.Biochem J. 2008 Jun 15;412(3):399-413. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080035. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18498250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Haematopoietically-expressed homeobox transcription factor: roles in development, physiology and disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 16;14:1197490. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1197490. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37398663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for a role of the polysaccharide capsule transport proteins in pertussis pathogenesis.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 12;9(12):e115243. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115243. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25501560 Free PMC article.
-
Misregulation of the proline rich homeodomain (PRH/HHEX) protein in cancer cells and its consequences for tumour growth and invasion.Cell Biosci. 2016 Feb 13;6:12. doi: 10.1186/s13578-016-0077-7. eCollection 2016. Cell Biosci. 2016. PMID: 26877867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Misteli T. Concepts in nuclear architecture. Bioessays. 2005;27:477–487. - PubMed
-
- Goldman RD, Gruenbaum Y, Moir RD, Shumaker DK, Spann TP. Nuclear lamins: building blocks of nuclear architecture. Genes Dev. 2002;16:533–547. - PubMed
-
- Yasui D, Miyano M, Cai S, Varga-Weisz P, Kohwi-Shigematsu T. SATB1 targets chromatin remodelling to regulate genes over long distances. Nature. 2002;419:641–645. - PubMed
-
- Kaiser TE, Intine RV, Dundr M. De novo formation of a subnuclear body. Science. 2008;322:1713–1717. - PubMed
-
- Shevtsov SP, Dundr M. Nucleation of nuclear bodies by RNA. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:167–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

