Effects of restricted fructose access on body weight and blood pressure circadian rhythms
- PMID: 22536215
- PMCID: PMC3321444
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/459087
Effects of restricted fructose access on body weight and blood pressure circadian rhythms
Abstract
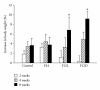
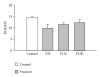
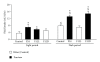
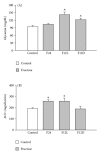
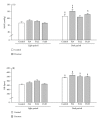
High-fructose diet is known to produce cardiovascular and metabolic pathologies. The objective was to determine whether the timing of high fructose (10% liquid solution) intake affect the metabolic and cardiovascular outcomes. Male C57BL mice with radiotelemetric probes were divided into four groups: (1) 24 h water (control); (2) 24 h fructose (F24); (3) 12 h fructose during the light phase (F12L); (4) 12 h fructose during the dark phase (F12D). All fructose groups had higher fluid intake. Body weight was increased in mice on restricted access with no difference in total caloric intake. Fasting glycemia was higher in groups with restricted access. F24 mice showed a fructose-induced blood pressure increase during the dark period. Blood pressure circadian rhythms were absent in F12L mice. Results suggest that the timing of fructose intake is an important variable in the etiology of cardiovascular and metabolic pathologies produced by high fructose consumption.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salt consumption increases blood pressure and abolishes the light/dark rhythm in angiotensin AT1a receptor deficient mice.Physiol Behav. 2006 Jun 15;88(1-2):95-100. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.03.008. Epub 2006 Apr 27. Physiol Behav. 2006. PMID: 16643970
-
Circadian rhythms of blood pressure, heart rate, and locomotor activity in spontaneously hypertensive rats as measured with radio-telemetry.Physiol Behav. 1994 Apr;55(4):783-7. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(94)90060-4. Physiol Behav. 1994. PMID: 8190809
-
Nocturnal hypertension in mice consuming a high fructose diet.Auton Neurosci. 2006 Dec 30;130(1-2):41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2006.05.006. Epub 2006 Jul 13. Auton Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16843071
-
Long term rebaudioside A treatment does not alter circadian activity rhythms, adiposity, or insulin action in male mice.PLoS One. 2017 May 5;12(5):e0177138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177138. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28475596 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive Induction of Type 2 Diabetes: Effects of a Reality-Like Fructose Enriched Diet in Young Wistar Rats.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 22;11(1):e0146821. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146821. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26799836 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Timing of fructose intake: an important regulator of adiposity.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012 Jan;39(1):57-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05636.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22032284 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective effects of SGLT2 inhibitors are possibly associated with normalization of the circadian rhythm of blood pressure.Hypertens Res. 2017 Jun;40(6):535-540. doi: 10.1038/hr.2016.193. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Hypertens Res. 2017. PMID: 28100918 Review.
-
Rodent models to study the metabolic effects of shiftwork in humans.Front Pharmacol. 2015 Mar 24;6:50. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00050. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25852554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular changes in animal models of metabolic syndrome.J Diabetes Res. 2013;2013:761314. doi: 10.1155/2013/761314. Epub 2013 Mar 14. J Diabetes Res. 2013. PMID: 23691518 Free PMC article.
-
Early developmental exposure to high fructose intake in rats with NaCl stimulation causes cardiac damage.Eur J Nutr. 2016 Feb;55(1):83-91. doi: 10.1007/s00394-014-0826-5. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Eur J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 25564432
References
-
- Elliott SS, Keim NL, Stern JS, Teff K, Havel PJ. Fructose, weight gain, and the insulin resistance syndrome. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2002;76(5):911–922. - PubMed
-
- Bray GA, Nielsen SJ, Popkin BM. Consumption of high-fructose corn syrup in beverages may play a role in the epidemic of obesity. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2004;79(4):537–543. - PubMed
-
- Brown CM, Dulloo AG, Yepuri G, Montani JP. Fructose ingestion acutely elevates blood pressure in healthy young humans. American Journal of Physiology. 2008;294(3):R730–R737. - PubMed
-
- Farah V, Elased KM, Chen Y, et al. Nocturnal hypertension in mice consuming a high fructose diet. Autonomic Neuroscience. 2006;130(1-2):41–50. - PubMed
-
- Furuhashi M, Ura N, Takizawa H, et al. Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system decreases adipocyte size with improvement in insulin sensitivity. Journal of Hypertension. 2004;22(10):1977–1982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

